- *Corresponding Author:
- Sadhana Rajput
Department of Pharmacy, G. H. Patel Building, Donor’s Plaza, The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, Fatehgunj, Vadodara-390 002, India
E-mail: sjrajput@gmail.com
| Date of Submission | 6 April 2010 |
| Date of Revision | 20 September 2011 |
| Date of Acceptance | 26 September 2011 |
| Indian J Pharm Sci, 2011, 73 (5): 583-586 |
Abstract
A simple, sensitive and highly selective electrochemical method was developed for the simultaneous determination of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin in aqueous media (Britton-Robinson buffer, pH-8.36) on a hanging mercury drop electrode (HMDE) using differential pulse polarography (DPP). Using DPP a separation of about 936 mV between the peak oxidation potentials of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin present in binary mixtures was obtained. The quantification limits for the simultaneous determination of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin were 0.083 μg/ml and 0.208 μg/ml, respectively. The proposed method was successfully applied for the simultaneous determination of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin in bulk drug and pharmaceutical tablet formulation.
Keywords
Method development, nitazoxanide, ofloxacin, voltammetry
Nitazoxanide is chemically N-(5-nitro-2-thiazoyal) salicylamide acetate) [1-4]. It is used as an antiprotazoal, antihelmenthic, in giardiasis and cryptosporidiosis, in immune-compromised patients, including those with HIV infection [2-4]. It is not official in any pharmacopoeia. Analytical methods reported for quantitative determination of nitazoxanide are spectrophotometric method [5], RP-HPLC method [6,7] and stability indicating RP-LC method [8].
Ofloxacin is chemically (±)-9-flouro-2,3-dihydro- 3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7-Hpyridal( 1,2,3de-)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylicacid and belongs to fluoroquinolone group of antimicrobial agents [2,9]. It is used in chlamydia or chlamydophila infection including nongonococcal urethritis. Ofloxacin is official in BP [10], USP [11], and EP [12]. The assay procedures mentioned in these pharmacopoeias are nonaqueous titration. Reported methods for quantitative determination of ofloxacin in pharmaceutical formulation or biological fluids are differential pulse polarography [13], square wave voltammetry [14], capillary electrophoresis [15], cyclic voltammetry, linear sweep voltammetry and electrochemical impendence spectroscopy [16], spectrophotometry [17] and HPLC [18-20]. Capillary electrophoresis [21], LC with fluorescence detection [22] and fluorimetry [23] are also reported for determination of ofloxacin enantiomers. Stability studies of ofloxacin are also reported [24]. Reported methods for simultaneous determination of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin are simultaneous equation method [25,26] and RP-HPLC method [27,28]. LOQ data is not available for simultaneous equation method but the RP-HPLC method reported LOQ as 0.43 μg/ml and 1.8 μg/ml for nitazoxanide and ofloxacin, respectively. Hence attempts were made to develop more sensitive and selective method for simultaneous determination of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin in bulk drug and pharmaceutical formulation.
All the reagents used were of AR grade. Pure drug samples of ofloxacin and nitazoxanide were kindly gifted by Alembic Pharmaceutical Limited (Vadodara, Gujrat, India) India. The gift samples were used as standards without further purification. Formulation Zenflox NT was purchased from local market.
All the electrochemical experiments were conducted in a three electrode single compartment glass cell. An Ag/AgCl (3.0 mol/L KCl) electrode was used as reference electrode and auxiliary electrode was a Pt electrode. The working electrode was a hanging mercury drop. The polarographic measurements were carried out using Metrohm 757 VA Computrace system (5.757.0010) attached to VA Computrace software 1.0 (Metrohm Ltd., Switzerland).
Ofloxacin stock solution (1 mg/ml) was prepared by dissolving 50 mg of ofloxacin in methanol. Ofloxacin working standard solution (100 mg/ml) was prepared by diluting 5 ml of ofloxacin stock solution upto 50 ml. Nitazoxanide stock solution (1mg/ml) was prepared by dissolving 50 mg of nitazoxanide in 50 ml of methanol. Nitazoxanide working standard solution (100 mg/ml) was prepared by diluting 5 ml of nitazoxanide stock solution upto 50 ml. Binary mixture solutions containing ofloxacin and nitazoxanide in a ratio same as that in commercial formulation available were prepared by mixing and diluting suitable aliquots of ofloxacin working standard solution and nitazoxanide working standard solution with methanol.
Twenty tablets were accurately weighed and powdered in a mortar. An amount equivalent to one tablet (containing 200 mg of ofloxacin and 500 mg nitazoxanide) was taken in 50 ml volumetric flask and dissolved in 50 ml methanol by sonicating it for five minutes. Then the solution was filtered through Whatman filter paper No. 40 to the 100 ml volumetric flask and volume was made up to the mark with methanol. The sample solution thus prepared was diluted with methanol to get the solution containing 25:62.5 μg/ml ofloxacin:nitazoxanide.
After optimizing all the experimental parameters, standard addition method was used for polarographic determination of ofloxacin and nitazoxanide at pH- 8.36. For this, 15 ml of supporting electrolyte Britton- Robinson buffer of pH-8.36 was taken in sample cell, purged for 300 s with N2 gas and the polarogram was recorded in the voltage range of -0.05 mV to -1.45 mV for blank measurement in DPP mode. Then appropriate amount of binary mixture solution was added to the same sample cell containing 15ml of supporting electrolyte Britton-Robinson buffer of pH-8.36 and scanned in the same range in DPP mode. In same manner five readings were obtained with two replications. Validation parameters like precision, accuracy, LOQ and robustness were studied as per ICH guidelines [29].
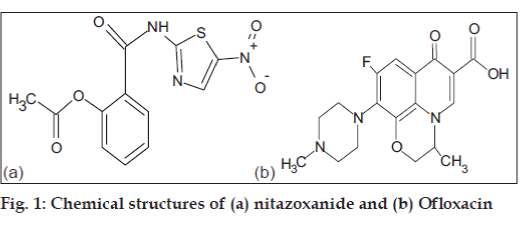
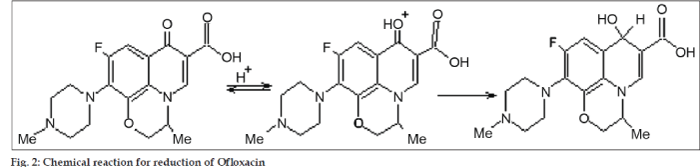
Nitazoxanide has nitro group in its structure (fig. 1). Study of nitazoxanide through electrochemical behaviour was possible due to reduction of nitro group to amino group. Ofloxacin (fig. 1) has been a subject of several electrochemical investigations. Belal et al. [17] have recently studied ofloxacin electrochemical behaviour by means of differential pulse polarography (DPP). They found that electrochemical activity of ofloxacin is due to the reduction of the carbonyl C=O group and it proceeds in two steps (fig. 2).
The effect of supporting electrolytes like 0.1 mM potassium chloride, acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer of pH-6, ammonia-ammonium chloride of pH-8, disodium hydrogen phosphate-potassium dihydrogen phosphate of pH-8 and Britton-Robinson buffer (pH-4 and pH-8.36) on the current was examined.
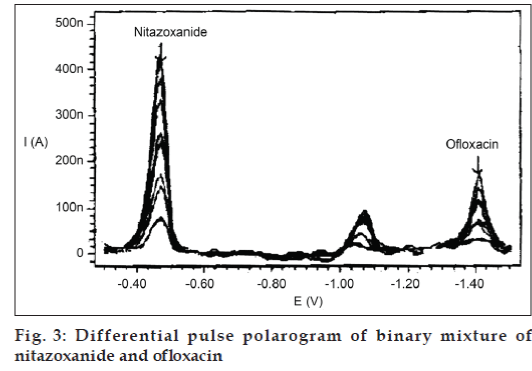
The experimental result shows that the peaks were not obtained for both the compounds in case of ammoniaammonium chloride of pH-8 and disodium hydrogen phosphate-potassium dihydrogen phosphate of pH-8 while in other cases cathodic reduction peaks for both the compounds were obtained. However, peaks were more sensitive and clear in case of Britton-Robinson buffer of pH-8.36 (fig. 3).
Working parameters of DPP method were established and effect of deposition potential, pulse amplitude voltage step time was studied. The best polarogram was obtained with deposition potential -1.3 V, deposition time 60 s, drop size 4, equilibrium time 10 s, voltage step 0.009 V, pulse amplitude 0.06 V and voltage step time 0.2 s (Table 1).
| Parameter | Optimized value |
|---|---|
| Electrode | HMDE |
| Cleaning potential | -0.3 V |
| Deposition potential | -1.5 V |
| Deposition time | 60 s |
| Voltage step | 0.004 V |
| Pulse amplitude | 0.04 V |
| Pulse time | 0.05 s |
| Voltage step time | 0.2 s |
| Equilibrium time | 10 s |
| Drop size | 4 |
Table 1: Working conditions for differential pulse polarographic analysis of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin
Interday and intraday precision for Differential Pulse Polarography method was measured in terms of % RSD. The experiment (preparation of calibration curve) was repeated five times in a day for intra-day and on five different days for inter-day precision (Table 2).
| Parameter | Ofloxacin | Nitazoxanide |
|---|---|---|
| Precision (%RSD) | ||
| Intraday(n=5) | 1.141 | 0.603 |
| Interday(n=5) | 1.378 | 0.458 |
| Accuracy | 98.39±0.77 | 98.39±1.17 |
| LOQ | 0.208µg/ml | 0.083 µg/ml |
| Robustness(%RSD) | 0.603 | 0.4996 |
LOQ = Limit of quantification. RSD = Relative standard deviation.
Table 2: Summary of validation parameters for proposed dpp method
Accuracy of the proposed method was studied by recovery studies. Recovery studies were carried out by addition of known of standard drugs solution of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin to preanalysed tablet solution. The resulting solution was analyzed by proposed method. Recovery studies were carried out at the 80%, 100% and 120% level of the label claim. Results of recovery studies and percentage recovery were found to be satisfactory (Table 2). The minimum concentrations of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin which could be quantified were 0.083 μg/ml and 0.208 μg/ ml, respectively.
The robustness of the method was determined by using different solvents for the preparation of stock solution of standard drug. The drug stock solution was prepared in methanol and 0.1M methanolic NaOH. The average value of %RSD of the responses for determination of ofloxacin and nitazoxanide were less than 2% reveals the robustness of the method.
Applicability of the proposed DPP method was determined by analyzing the commercially available tablets containing nitazoxanide and ofloxacin a
nd results were found to be in good agreement with the label claim (Table 3).
| Formulation ; | Drugs | Labeled claim mg/ tablet | Amount* found (mg) | % Found±SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1* DT | Nitazoxanide | 500 | 492.80 | 98.56±0.61 |
| Ofloxacin | 200 | 196.41 | 98.20±0.94 |
*Average of five determinations SD = Standard deviation
Table 3: Assay results for combined dosage form using proposed dpp method
The obtained results show that the proposed DPP method is simple, accurate, precise as well as sensitive and can be used for the quantitative determination of ofloxacin and nitazoxanide alone or in mixture without any prior separation of individual drug. The method was found to be more sensitive than the HPLC method reported for the simultaneous estimation of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin. The value of %RSD for intraday and interday precision was found less than 2. This value confirms that method is precise. The value of % recovery greater than 98% for this method shows that the method is accurate and free from the interference of excipients used in formulation.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Alembic Pharmaceutical Limited (Vadodara, Gujarat, India) for supplying gift samples of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin.
References
- Sweetman SC, Editors. Martindale: The complete drug reference. 33rd ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press; 2002. p. 598.
- O’Neil MJ. The Merck Index, An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. NJ; Whitehouse Station: 2001.
- Cavier R. Nitazoxanide in treatment of anthelminthiasis. Eur J Med ChemChimTher 1978;13:539-49.
- Murphy JR, Friedmann JC. Pre-clinical toxicology of nitazoxanide-a new antiparasitic compound. J ApplToxicol 1985;5:49-52.
- Narayana LK, Manohara YN, Appala RS. Spectrophotometric determination of nitazoxanide. Indian Drugs 2007;44:145-8.
- Narayana LK, Manohara YN, Appala RS. Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for the estimation of nitazoxanide in bulk drugs and tablets. Indian Drugs 2006;43:503-6.
- Jadhav VY, Gandhi SV, Dhavale ND, Sabnis SS. RP-HPLC Determination of nitazoxanide in bulk and different tablet formulations. Eurasian J Anal Chem 2008;3:404-9.
- Jadhav AS, Pathare DB, Shingare MS. A Validated stability indicating RP-LC method for nitazoxanide, a new antiparasitic compound. Chromatographia 2007;66:595-600.
- Parfitt K, Editors., In; Martindale; The Complete Drug Reference, 33rd Ed., London: The Pharmaceutical Press; 2002. p. 615.
- British Pharmacopoeia, Vol. 1, London: The British Pharmacopoeia Commission; 2002. p. 1247.
- United State Pharmacopoeia, Vol. XXIV, Supplement 1, Rockville, MD: The United States Pharmacopoeial Convention, Inc; 2000. p. 1215.
- European Pharmacopoeia, Strasbourg, France: Council of Europe; 2005. p. 2131.
- Rizk M, Belal F, Aly FA, El-Enany NM. Differential pulse polarographic determination of ofloxacin in pharmaceuticals and biological fluids. Talanta 1998;46:83-9.
- Gulaboski R, Jordanoski R. Square Wave Voltammetry of Ofloxacin. Bull ChemTechnolMacedoni 2000;19:179-81.
- Kowalski P, Plenis A. Simultaneous Determination of Six Quinolone Antibiotics in Poultry and Porcine Samples by Capillary Electrophoresis. Bull Vet InstPulawy 2008;52:81-5.
- Yang C, Zhang S, Liu Y, Huang W. Electrochemical behaviors of ofloxacin and its voltammetric determination at carbon nanotubes film modified electrode. Front Chem China 2008;3:353-8.
- Wankhede SB, Prakash A, Chitlange SS. Simultaneous Spectrophotometric Estimation of Ofloxacin and Satranidazole in Tablet Dosage Form. Asian J Research Chem 2008;1:9-11.
- Shinde VM, Desai BS, Tendolkar NM. Selective determination ofFluoroquinolones from tablets by Reverse Phase HPLC. Indian Drugs 1998;35:715-7.
- Argekar AP, Kapadia US, Raj SV, Kunjir SS. Quantitative Determination of Lomefloxacin, Ofloxacin, Pefloxacin and Enrofloxacin in Pharmaceutical dosages, Bulk Drugs and Process monitoring of Enrofloxacin by HPLC-RP. Indian Drug 1996;33:261-6.
- Krishnaiah YS, Indira Muzib Y, Bhaskar P. In Vivo Evaluation of Guar Gum-based Colon-targeted Drug Delivery Systems of Ornidazole in Healthy Human Volunteers. J Drug Targeting 2003;11:109-15.
- Elbashir AA, Sadd B, Ali A, Saleh M, Aboul-Enein H. Determination of Ofloxacin Enantiomers in Pharmaceutical Formulations by Capillary Electrophoresis. J LiqChromatogrRel Tech 2008;31: 348-60.
- Shao B, Sun X, Zhang J, Hub J, Dong H, Yanga Y. Determination of ofloxacin enantiomers in sewage using two-step solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 2008;1182:77-84.
- Gurumurthy P, Ramachandran G, Hemanthkumar AK, Venkatesan P, Chandrasekaran V, Narayanan PR. Simple spectrofluorometric and microbiological assay methods for the estimation of ofloxacin in biological fluids. Indian J Phamacol 1998;30:263-6.
- Bakshi M, Singh B, Singh A, Singh S. The ICH guidance in practice: stress degradation studies on ornidazole and development of stability indicating assay. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2001;26:891-7.
- Senthilraja M. Simultaneous UV Spectrophotometric method for the estimation of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin in combined dosage form. Res J Pharm Tech 2008;1:469-71.
- Mahaparale SP, Mahaparale PR, Sangshetti JN, Deshpande SV. Simultaneous spectrophotometric estimation of ofloxacin and nitazoxanide in tablet dosage form. Indian Drugs 2009;46:354-7.
- Kalta RR, Sharma R, Chaturvedi SC. Simultaneous RPHPLC determination of nitazoxanide and ofloxacin in combined tablet dosage form. Indian J PharmaSci 2008;70:491-3.
- Lalitha KG, Venkatachalam T, Srinivasan R, Kalaiselvi P. Simultaneous estimation of ofloxacin and nitazoxanide in tablets by RP HPLC method. Indian Drugs 2009;46:32-6.
- ICH Guidance on analytical method validation, International convention on quality for the pharmaceutical industry, Toronto, Canada; 2002