- *Corresponding Author:
- V. Mishra
School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Lovely Professional University, Phagwara, Punjab 144411, India
E-mail: vijaymishra2@gmail.com
| Date of Received | 21 September 2023 |
| Date of Revision | 19 March 2023 |
| Date of Acceptance | 15 July 2024 |
| Indian J Pharm Sci 2024;86(4):1331-1340 |
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms
Abstract
The study was designed to develop a simple, precise, rapid and reproducible simultaneous method for fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine in dendrimer-carbon nanotube conjugates. Reverse phase column C18 was used for the development and validation of the high-performance liquid chromatography method. The method was run on isocratic mode with methanol and water (80:20) with 1 ml/min flow rate and the detection was carried out at 258 nm. Fosamprenavir calcium was shown to have a retention time of 4.255 min whereas nevirapine had a retention time of 6.337 min. The method was validated as per International Council for Harmonisation M10 guidelines. The coefficient of correlation (R2) was found to be 0.9905 for fosamprenavir calcium and 0.9896 for nevirapine. The approach was accurate and precise based on drug recovery (greater than 95 %) and relative standard deviation (less than 2 % among duplicate experiments). Lower, medium and higher quantified concentration of fosamprenavir calcium were found to be 5.98 μg/ ml, 7.18 μg/ml and 8.38 μg/ml respectively and for nevirapine the lower, medium and higher quantified concentration were found to be 6.54 μg/ml, 7.74 μg/ml and higher quantified concentration 8.94 μg/ml respectively. Drug loading was found to be 47.59 % for fosamprenavir calcium and 69.65 % for nevirapine when both drugs are loaded together in dendrimer-carbon nanotube conjugates. From the study, it can be concluded that a robust method was developed that qualified different validation parameters and can be used for the determination of fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine in dendrimer-carbon nanotube conjugates.
Keywords
Fosamprenavir calcium, nevirapine, simultaneous method development, high-performance liquid chromatography, dendritubes
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is the virus responsible for the development of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). The disease was discovered in the year 1981, till mid-1990’s every person who are infected by the disease lost their life as effective therapeutics were not available. In the past few decades, with the advancement of anti-viral drugs the infection is quite manageable but the cure is still not achieved. The virus tends to develop resistance against a single drug very easily[1]. Hence the cocktail therapy was started termed Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART). HIV is specifically targeting the immune cells especially the CD4+ receptor of T cells with the help of its surface protein gp120. The virus can adapt to different cells and varying growth environments. It can develop resistance against available drugs; hence combination therapy is used to avoid resistance[2,3].
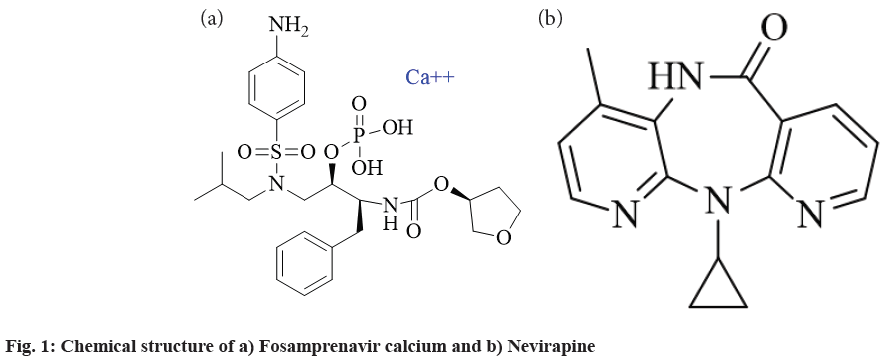
Fosamprenavir calcium is a prodrug of amprenavir and belongs to the class of protease inhibitors. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name of fosamprenavir is (1S,2R)-3-[[(4- aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]- 1-(phenylmethyl)-2-(phosphonooxy)propyl] carbamic acid C-[(3S)-tetrahydro-3-furanyl]ester calcium salt. The structure of the drug fosamprenavir calcium is shown in fig. 1. Fosamprenavir calcium is marketed as an oral suspension or coated tablet. As per BCS, fosamprenavir calcium has low solubility and high permeability making it a candidate of the Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) class II. Lexiva is the brand name of the fosamprenavir calcium with a dose of 700 mg two times a day[4,5].
Nevirapine is a drug that causes inhibition of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase enzyme. IUPAC name of Nevirapine is 1-cyclopropyl-5,11- dihydro-4-methyl-6H-dipyrido [3,2- b:2',3'-e] [1,4] diazepin-6-one. The structure of nevirapine is shown in fig. 1. It can interfere with polymerase activity which is involved in the production of both ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid by binding on an allosteric site on reverse transcriptase. It is official in British Pharmacopeia and United States Pharmacopoeia. Nevirapine is a potent inductor of enzymes and leads to a reduction of plasma concentration of other drugs. It gets rapidly metabolized by Cytochrome P450 3A4. Nevirapine belongs to BCS class II. The brand name of nevirapine tablets is Viramune[6].
The research work was carried out to develop a simple, fast, sensitive, economic isocratic method for simultaneous determination of fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The developed method was validated with different parameters including precision, specificity, robustness, accuracy, linearity and range. The method was applied for the estimation of the concentration of two drugs fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine in the formulated dendrimer conjugated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs).
Materials and Methods
Fosamprenavir calcium was procured as a gift sample from Lupin Pharmaceuticals and nevirapine was procured as a gift sample from Emcure Pharmaceuticals. HPLC-grade acetronitrile and methanol were purchased from Rankem, Maharashtra, India. COOH-MWCNTs were purchased from Adnano Technologies, Machenahalli, Karnataka. All the other chemicals such as formic acid and acetic acid were of analytical grade from Sigma chemicals.
Spectral analysis:
10 μg/ml solution of drugs fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine were prepared separately using methanol. The samples were scanned against methanol as blank in the range of 190-400 nm using Ultraviolet (UV) spectrometer-1800 (Shimadzu, Japan). The physical mixture of 10 μg/ml of both drugs was prepared and also scanned using UVspectrometer[ 7].
Method development:
A simultaneous HPLC method of two drugs fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine was developed (Shimadzu LC-20AD Prominence, Japan) using the nucleodur C18 column. The dimensions of the column were 250 mm × 4.6 mm and the size of the bead is 5 μm. The detector used was a photodiode array detector (SPD-M20A; Shimadzu, Japan) and a rheodyne injector (7725i). The pump used is the LC20AD pump. LabSolution version 5.82 was used for chromatographic integration, recording and statistical evaluation. The flow of the solvent system was adjusted to 1 ml/min. The volume was adjusted to 20 μl for the sample injection.
The mobile phase used for isocratic elution is methanol and water in the ratio of 80:20. Different solvent system was used for the elution of the two drugs fosamprenavir and nevirapine in the chromatogram. The composition of the solvent system for the mobile phase was selected based on chromatographic peak parameters such as peak purity, sharpness, resolution and tailing factors of the peaks. The solvent system should support the complete resolution of two peaks. Different trials were carried out to better elution of the two drugs. Solvent mixtures used for method development are buffer:methanol, buffer:Acetonitrile (ACN), formic acid:ACN, formic acid:methanol and methanol:water.
Preparation of the stock solution for fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine:
Accurately weighed 10 mg of fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine was placed in a volumetric flask of 10 ml. 2 ml of methanol was added to this flask and mixed well till the drug is dissolved. The final volume was made up to 10 ml with methanol[8].
Preparation of the working solution:
From the stock solution, 1 ml of aliquot was taken and sifted into a volumetric flask of 10 ml and made the volume using methanol up to 10 ml to get the concentration of 100 μg/ml. 100 μg/ml working solution was prepared from the above solution by withdrawing 1 ml of stock solution and transferring it to a volumetric flask of 10 ml. The final concentration of the working solution was 10 μg/ml for both drugs fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine[8].
Method validation:
The optimization of the simultaneous HPLC method of fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine has been validated. Validation was performed as per ICH 45 guidelines Q2(R1). Validation of the method was carried out by evaluating different parameters such as range and linearity, Limit of Quantification (LOQ) and Limit of Detection (LOD), robustness, precision and accuracy. The method was also studied for system suitability parameters[9].
System suitability:
A blank mobile phase was injected for the calculation of system suitability. Six replicates of the fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine mixture were injected into the HPLC system. System suitability parameters such as tailing factors, theoretical plate number and height of the theoretical plate. The method should be able to resolve the peaks of two drugs fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine[10].
Preparation of calibration curve:
The standard working solution was used to prepare the calibration curve. From the 10 μg/ml working solution, further dilution was made of different concentrations such as 2.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0 and 10.0 μg/ml. The dilution was made by withdrawing 2.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0, and 10.0 ml of working stock solution in the five different flasks of 10 ml and the final volume was adjusted up to 10 ml using methanol. The prepared dilutions were analyzed using HPLC. The area of the peak was used for the plotting of the calibration curve with peak area on the Y-axis and concentration on the X-axis. The mean peak area is calculated for each concentration by injecting the samples (6 times). This HPLC method will assist in the determination of the intercept, slope and correlation coefficient of the calibration curve[10].
Linearity and range:
For linearity and range, the peak area for each concentration was plotted against concentration. The plotted graph helps to determine the intercept, the correlation coefficient of the calibration curve and the slope[10].
Accuracy study:
The absolute recovery of two drugs was determined for calculating the recovery of the method[10]. The absolute recovery was calculated by quantifying two drugs at three different levels Lower Quantified Concentration (LQC) (80 %), Medium Quantified Concentration (MCQ) (100 %) and Higher Quantified Concentration (HQC) (120 %) of the middle concentration of the plotted curve. For fosamprenavir mid concentration was 7.18 μg/ ml and for nevirapine mid concentration was 7.74 μg/ml. In case of fosamprenavir calcium the LQC is 5.98 μg/ml, MQC 7.18 μg/ml and HQC is 8.38 μg/ml and for nevirapine the LQC is 6.54 μg/ml, MQC is 7.74 μg/ml and HQC is 8.94 μg/ml[11].
Precision studies:
The precision study includes repeatability (intraday) and intermediate precision (interday). The samples of LQC, MQC and HQC were injected six times under the same experimental condition on the same day. The intermediate precision includes intraday precision, interday precision and interanalyst. The interday studies were performed by injecting six times LQC, MQC and HQC samples for 3 consecutive d, intra-day was determined by injecting LQC, MQC and HQC samples six times at different times on the same day and interanalyst was carried out by different analyst by injecting six times LQC, MQC and HQC. Precision studies were carried out under the same experimental conditions on the same day[10].
Absolute recovery=Actual concentration recovered/Theoretical concentration×100
Determination of LOD and LOQ:
For calculation, fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine were carried out based on the standard deviation of the intercept and slope with the help of a linear regression equation. The equation for the calculation of LOD and LOQ is given below. LOD=3.3Q/S and LOQ=10 Q/S
Robustness:
Robustness was carried out by making minute changes deliberately such as wavelength and flow rate in the chromatographic conditions. Robustness was studied for both the drugs fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine and assessed for resolution peaks, tailing factor and number of theoretical plate[10].
Drug loading in dendritubes (Dendrimers conjugated carbon nanotubes):
Accurately weighed 200 mg of nevirapine was taken in a flask. To this methanol, 20 ml was added and the system was mixed well. The drug methanol solution was sonicated using a bath sonicator for 10 min to dissolve the drug completely. 200 mg of fosamprenavir calcium was added to the above solution. The mixture was sonicated for 2 min to solubilize the drug. The prepared solution was shifted to a round bottom flask. To this accurately weighed 400 mg of dendritubes was added to the above mixture. The preparation was stirred with a magnetic stirrer for 48 h. After 48 h, the resultant solution was dialyzed with a dialysis bag (MWCO 6000-7000 Da, Sigma, USA) using methanol:water (2:1) for 15 min. During dialysis sink condition was maintained. The resultant product was collected and dried at 50° till it is completely dried. The dried product is collected and stored in an air-tight container for further characterization[11,12].
Results and Discussion
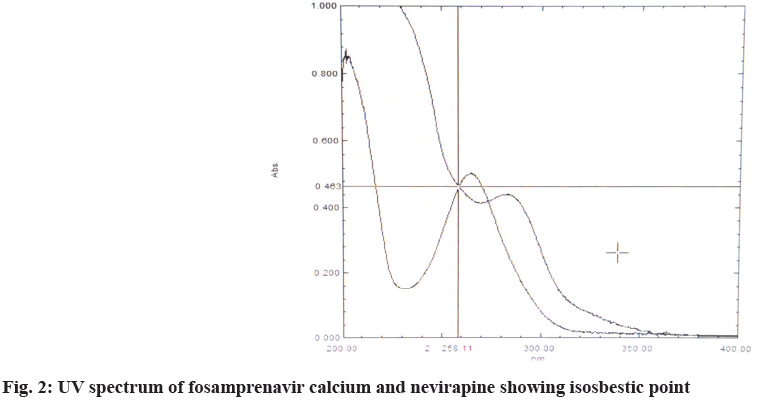
10 μg/ml solution was prepared and scanned at 400-200 nm using a UV spectrophotometer. For fosamprenavir calcium, the absorption maxima were found to be 265 nm and for nevirapine, the absorption maxima were found to be 283 nm. The isosbestic point of two drugs in a mixture of the two drugs was found to be 258 nm. The UV scan results are shown in fig. 2. Method development and validation were carried out at 258 nm.
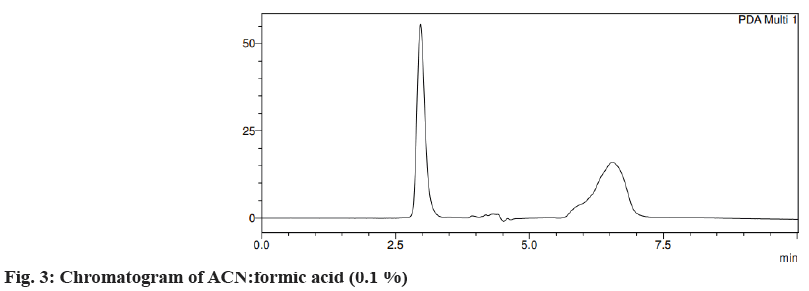
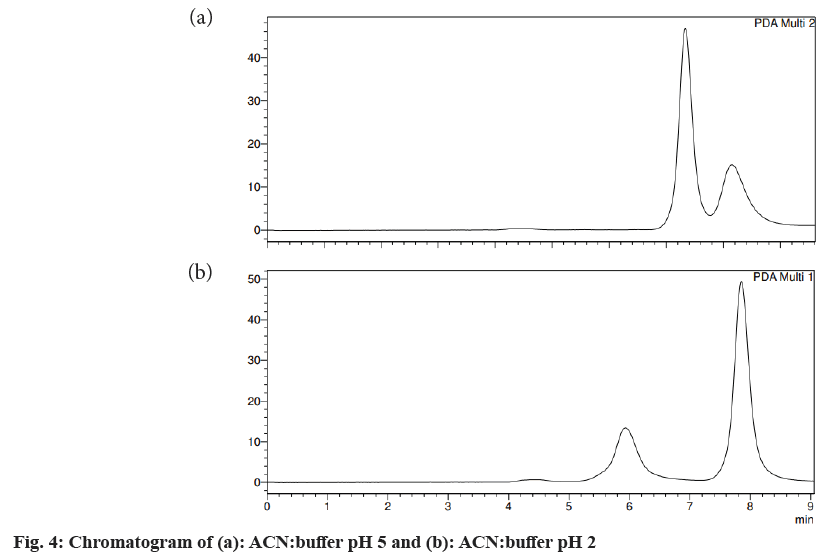
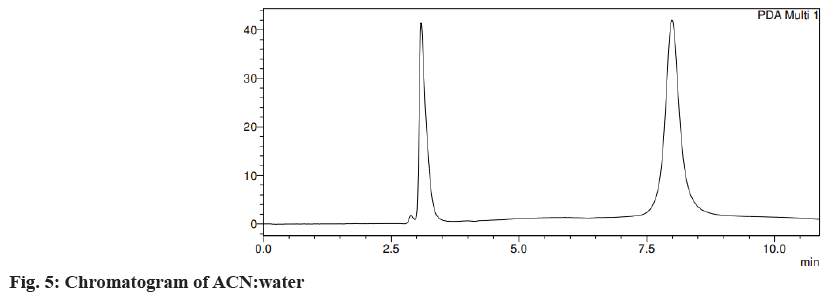
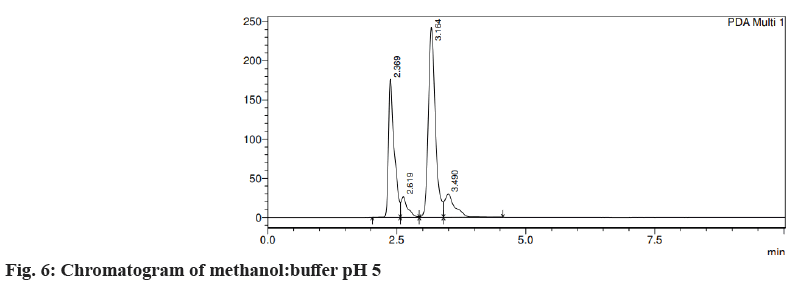
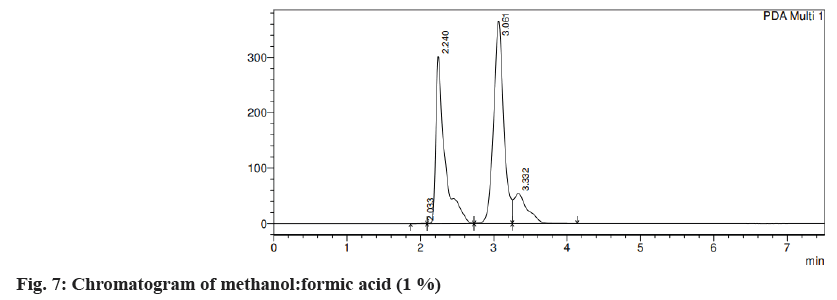
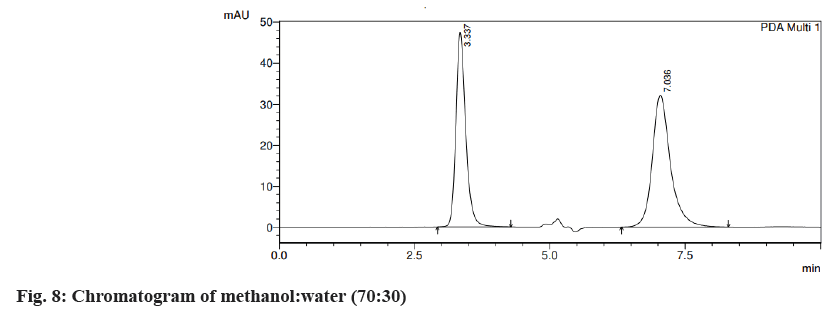
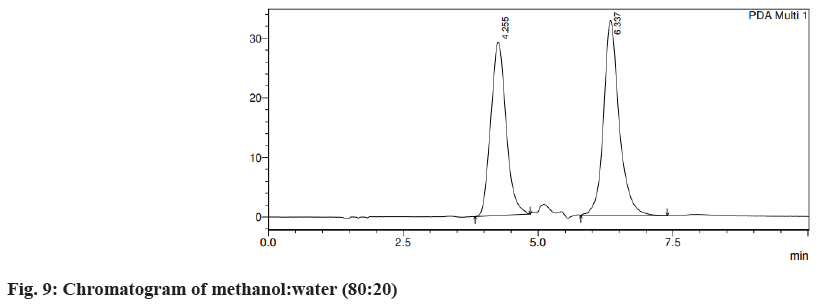
Different trials were carried out using different solvent systems in varying ratios for the isolation of two drugs and the results were analyzed. The retention time of drugs tends to change with changes in mobile phase. Trial 1, ACN:formic acid (0.1 %) (fig. 3) in the different ratios was carried out and the resultant peaks were broad. In trial 2, ACN:buffer pH 5 (fig. 4a) and ACN:buffer pH 2 (fig. 4b) were used, at 90:10 and 60:40 no peak was observed, with a 40:60 peak with a broad tail was observed. Trial 3, ACN:water (40:60) (fig. 5) peak was observed but tends to retain the drug. In trial 4, Methanol buffer at varying ratios was used sharp peak was observed but with tails (fig. 6). Trail 5, methanol:formic acid 0.1 % (fig. 7), a peak was observed but has a broad tail. Trial 6, methanol:water (70:30) (fig. 8) peaks were resolved properly at retention times 3.352 and 7.042 for fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine respectively. When methanol:water (80:20) (fig. 9) was used good peaks were observed at 3.385 and 6.509. The peak is sharper than the peak observed at methanol:water 70:30 for the drug nevirapine at a flow rate of 1 ml/min. Thus, the solvent system methanol:water (80:20) (fig. 10) was finalized for method development and validation.
A system suitability test was performed to determine column efficiency, repeatability and resolution of the specific chromatographic system to confirm its ability for a specific analysis method. It helps to study the applicability of the chromatographic system and its effectiveness. Chromatographic conditions tend to change continuously when the system is used regularly which alters the reproducibility of analytical methods. The lower height equivalent to a theoretical plate, tailing factor value less than 2 and theoretical plate value>2000 confirm better column efficiency. The result obtained indicated that the developed method has good system suitability. There is no extra peak observed in the chromatogram of drugloaded dendritubes supporting the specificity of the method for the estimation of both drugs[13]. System suitability parameters were shown in Table 1.
| S. No | Parameters | Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fosamprenavir calcium | Nevirapine | Limits | ||
| 1 | Theoretical plates | 1034.26 | 2606.77 | Depends on theoretical plates |
| 2 | Theoretical plates/meter | 6895.102 | 17819.581 | >20 000 |
| 3 | Height equivalent to a theoretical plate | 145.030 | 57.542 | >2000 |
| 4 | Tailing factor | 1.182 | 1.195 | >2 |
Table 1: Parameters of System Suitability for Fosamprenavir Calcium and Nevirapine
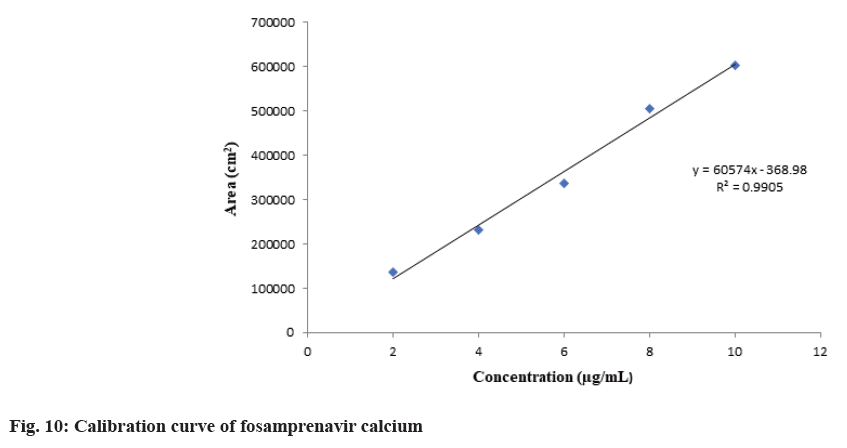
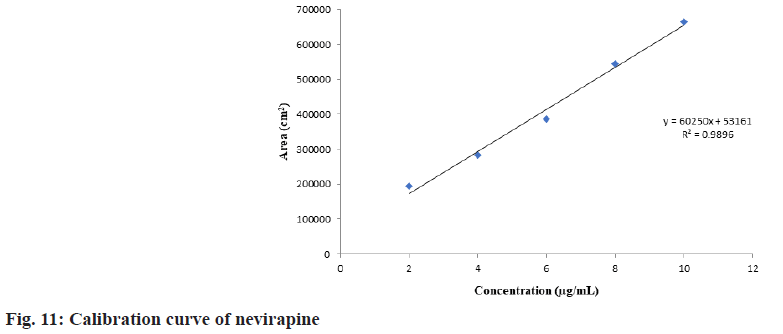
The calibration curve for fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine was plotted. The calibration curve was linear and found to be in a specified range of 2-10 μg/ml. R2 value represents the correlation coefficient was found to be 0.9905 for fosamprenavir calcium and 0.9896 for nevirapine. The calibration curves were shown in fig. 10 and fig. 11.
Recovery is an important validation parameter and applicable to all analytical methods. Recovery studies help to calculate the amount of analyte which can be extracted and can be measured from the analytical test material. Recovery studies were carried out in triplicate samples at three different concentrations, a midconcentration of the calibration curve (MQC), one higher (HQC) and one lower (LQC) than MQC by spiking the drug solution of known concentration. From the results, it was observed that recovery for all three concentrations was found to be in the range of 95 %-105 %, which falls within the prescribed limits[14].
Precision includes repeatability studies (intraday studies), interday for 3 d and interanalyst. Precision studies were carried out for fosamprenavir and nevirapine by injecting six injections of LQC, MQC and HQC in the same analytical condition.
From the obtained chromatographic peaks, the peak area was calculated. It was observed that the peak area was repeatable for interday and intraday analysis. Percentage Relative Standard Deviation (RSD) was calculated for intraday, interday and interanalyst studies at the same chromatographic condition by injecting six times HQC, MQC and LQC. The calculated % RSD was less than 2.0 which was within the acceptable limit. The data revealed that the developed method was precise[15]. Results for intraday (repeatability) and interday precision for fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine are given in Table 2.
| Drugs | Levels | Theoretical concentration of standard solution (µg/ml) | Recovered concentration (µg/ml) (mean±SD) (n=6) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) | Mean recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fosamprenavir calcium | LQC | 5.98 | 5.9189±0.1014 | 1.5414 | 98.9799 | 99.7657 |
| MQC | 7.18 | 7.1122±0.1167 | 1.559 | 99.0565 | ||
| HQC | 8.94 | 8.4856±0.1180 | 2.1453 | 101.2609 | ||
| Nevirapine | LQC | 6.54 | 6.5281±0.0984 | 1.5073 | 99.8190 | 99.6630 |
| MQC | 7.74 | 7.7650±0.0742 | 0.9567 | 100.3235 | ||
| HQC | 8.94 | 8.8368±0.1333 | 1.5107 | 98.8466 |
Table 2: Accuracy Study Results for Fosamprenavir Calcium and Nevirapine
The LOD was 0.277 μg/ml and 0.290 μg/ml for fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine, respectively, whereas, the LOQ was 0.839 μg/ml and 0.879 μg/ml for fosamprenavir calcium and nevirapine, respectively (Table 3).
| Parameters | Levels | Area 1 | Area 2 | Area 3 | Area 4 | Area 5 | Area 6 | Mean Area (cm2) | SD | % RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fosamprenavir Calcium | ||||||||||
| Repeatability (Intraday) | LQC | 345809 | 366106 | 357355 | 359659 | 354633 | 355676 | 356539.67 | 6075.062 | 1.703895 |
| MQC | 430543 | 430215 | 428138 | 435698 | 429876 | 432143 | 431102.17 | 2366.239 | 0.548881 | |
| HQC | 507627 | 508765 | 512345 | 501987 | 508734 | 518767 | 509704.17 | 5079.394 | 0.996538 | |
| Intermediate Precision | ||||||||||
| Interday 1 | LQC | 353978 | 349001 | 366008 | 366757 | 363166 | 356795 | 359284.17 | 6534.736 | 1.818821 |
| MQC | 430310 | 427788 | 437078 | 421263 | 421036 | 417148 | 425770.5 | 6703.45 | 1.574428 | |
| HQC | 506153 | 509164 | 502204 | 507535 | 491052 | 491529 | 501272.83 | 7366.32 | 1.469523 | |
| Interday 2 | LQC | 373880 | 364291 | 360541 | 358830 | 371134 | 360807 | 364913.83 | 5663.793 | 1.552091 |
| MQC | 447474 | 443668 | 440573 | 457260 | 463460 | 440552 | 448831.17 | 8663.045 | 1.930134 | |
| HQC | 507037 | 508305 | 500416 | 509182 | 500416 | 509182 | 505756.33 | 3843.707 | 0.759992 | |
| Interday 3 | LQC | 365489 | 368436 | 346319 | 357522 | 356746 | 359771 | 359047.17 | 7068.699 | 1.968738 |
| MQC | 434975 | 437046 | 425668 | 422957 | 426785 | 439137 | 431094.67 | 6183.284 | 1.434322 | |
| HQC | 510562 | 508823 | 503073 | 508447 | 504744 | 508945 | 507432.33 | 2622.893 | 0.516895 | |
| Interanalyst | LQC | 360757 | 360758 | 354587 | 352819 | 363568 | 354856 | 357890.83 | 3968.938 | 1.10898 |
| MQC | 425623 | 430123 | 439271 | 419470 | 428345 | 421956 | 427464.67 | 6388.571 | 1.494526 | |
| HQC | 504563 | 502341 | 510984 | 520341 | 515290 | 500043 | 508927 | 7261.127 | 1.426752 | |
| Nevirapine | ||||||||||
| Repeatability (Intraday) | LQC | 453421 | 447560 | 440658 | 460130 | 446681 | 445676 | 449021 | 6211.666 | 1.38338 |
| MQC | 514356 | 523987 | 529876 | 513056 | 523045 | 505674 | 518332.33 | 8075.942 | 1.558063 | |
| HQC | 595007 | 581505 | 591092 | 587609 | 593247 | 591265 | 589954.17 | 4402.178 | 0.74619 | |
| Intermediate Precision | ||||||||||
| Interday 1 | LQC | 444895 | 454543 | 457048 | 449892 | 432988 | 442737 | 447017.17 | 8012.089 | 1.792345 |
| MQC | 513483 | 520731 | 518472 | 519580 | 518341 | 505792 | 516066.5 | 5120.251 | 0.992169 | |
| HQC | 585427 | 591786 | 595444 | 585790 | 591756 | 597778 | 591330.17 | 4553.902 | 0.770112 | |
| Interday 2 | LQC | 447474 | 443668 | 440573 | 457260 | 463460 | 440552 | 448831.17 | 8663.045 | 1.930134 |
| MQC | 530918 | 536035 | 523677 | 524860 | 520616 | 528156 | 527377 | 5063.643 | 0.960156 | |
| HQC | 589133 | 585992 | 586540 | 597999 | 590729 | 597828 | 591370.17 | 4887.335 | 0.826443 | |
| Interday 3 | LQC | 436756 | 444161 | 450908 | 440916 | 430478 | 440872 | 440681.83 | 6275.62 | 1.424071 |
| MQC | 521692 | 532543 | 507066 | 522430 | 531910 | 526978 | 523769.83 | 8550.377 | 1.632468 | |
| HQC | 593265 | 589678 | 587730 | 587646 | 581314 | 597616 | 589541.5 | 5060.416 | 0.858365 | |
| Interanalyst | LQC | 457809 | 454937 | 444512 | 446349 | 435689 | 445896 | 447532 | 7233.07 | 1.616213 |
| MQC | 512384 | 521839 | 514829 | 519834 | 512834 | 521294 | 517169 | 3938.925 | 0.761632 | |
| HQC | 596294 | 589362 | 590017 | 596723 | 582396 | 571238 | 587671.67 | 8779.969 | 1.494026 |
Table 3: Precision Study Results for Fosamprenavir Calcium and Nevirapine
Robustness was carried out by intentionally altering the parameters including flow rate and wavelength of the developed chromatographic method. The study helps to provide accurate and precise results even in altered conditions. The developed method was evaluated for robustness and found that on changing the parameters such as flow rate and wavelength, no significant changes were observed which confirms that the method is robust and will not be affected by small changes in chromatographic conditions. Along with this peak symmetry was observed for both drugs found to be unaffected with a tailing factor of less than 2 and with good resolutions. % RSD was calculated for fosamprenavir and nevirapine and it was found to be less than 1 % confirming the robustness of the method (Table 4)[16].
| Variables | Value | Concentration (µg/ml) | Average area (cm2) | Standard Deviation | % RSD | % Recover |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fosamprenavir calcium | ||||||
| Flow rate | 0.8 | 10 | 603462 | 1417.7491 | 0.2349 | 99.6848 |
| 1 | 10 | 581272 | 2010.3046 | 0.3458 | 96.0215 | |
| 1.2 | 10 | 551290 | 2948.6353 | 0.5349 | 91.0719 | |
| Wavelength | 256 | 10 | 528365 | 688.0149 | 0.1302 | 87.2873 |
| 258 | 10 | 571295 | 2582.3540 | 0.4520 | 94.3745 | |
| 260 | 10 | 629845 | 1483.5100 | 0.2355 | 104.0403 | |
| Nevirapine | ||||||
| Flow rate | 0.8 | 10 | 643947 | 9122.3846 | 1.4166 | 9.7601 |
| 1 | 10 | 679384 | 1174.5044 | 0.1729 | 10.0246 | |
| 1.2 | 10 | 667406 | 678.1154 | 0.1016 | 10.1947 | |
| Wavelength | 256 | 10 | 669920 | 3545.4334 | 0.5292 | 10.3786 |
| 258 | 10 | 656295 | 2588.7179 | 0.3944 | 9.9371 | |
| 260 | 10 | 635757 | 2513.7646 | 0.3954 | 9.6853 |
Table 4: Robustness Study Results for Fosamprenavir Calcium and Nevirapine
In conclusion, it can be concluded that a reversephase HPLC simultaneous method was developed for the determination of fosamprenavir and nevirapine. The method was efficiently developed with good resolution and peak symmetry for both drugs. The method was validated using different parameters such as range and linearity, accuracy and precision. The study confirms that the method can be used to quantify drugs in different dosage forms, in biological samples during animal studies and clinical studies.
Conflict of interests:
The authors declared no conflict of interests.
References
- Lu DY, Wu HY, Yarla NS, Xu B, Ding J, Lu TR. HAART in HIV/AIDS treatments: Future trends. Infect Disord Drug Targets 2018;18(1):15-22.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dudekonda S, Narayanswami G. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Mount Sinai Expert Guides Crit Care 2021:480-90.
- Mishra V, Kesharwani P, Jain NK. siRNA nanotherapeutics: A Trojan horse approach against HIV. Drug Discov Today 2014;19(12):1913-20.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nevirapine. PubChem; 2023.
- Nekkala K, Kumar JS, Ramachandran D. Stability indicating RP-HPLC method for quantification of impurities in fosamprenavir calcium drug substance. J Pharm Sci Res 2019;11(3):712-7.
- Fosamprenavir Calcium. PubChem; 2023.
- Goku PE, Orman E, Quartey AN, Adu JK, Adosraku RK. A simple RP?HPLC method to simultaneously assay the contents of lamivudine, tenofovir, and nevirapine in fixed dose combined oral antiviral medicines. J Chem 2020;2020(1):4618360.
- Khursheed R, Singh SK, Kapoor B, Gulati M, Wadhwa S, Gupta S, et al. Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of curcumin and quercetin in extracts, marketed formulations, and self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system. GEN Open 2021;1(1):43-52.
- Guideline ICH. Validation of analytical procedures: Text and methodology Q2 (R1) 2005;1(20):5.
- Kumar R, Kumar R, Khursheed R, Awasthi A, Khurana N, Singh SK, et al. Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for estimation of fisetin in rat plasma. South Afr J Botany 2021;140:284-9.
- Mirali M, Jafariazar Z, Mirzaei M. Loading tacrine Alzheimer's drug at the carbon nanotube: DFT approach. Lab in silico 2021;2(1):3-8.
- Pruthi J, Mehra NK, Jain NK. Macrophages targeting of amphotericin B through mannosylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Drug Target 2012;20(7):593-604.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Awasthi A, Kumar A, Kumar R, Vishwas S, Khursheed R, Kaur J, et al. RP-HPLC method development and validation for simultaneous estimation of mesalamine and curcumin in bulk form as well as nanostructured lipid carriers. South Afr J Botany 2022;151:529-37.
- Mohanraj P, Sarkar DK, Choudhury T, Gauthaman K. A simple and rapid RP?HPLC method for the estimation of nevirapine in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage forms. J Chem 2008;5:1081-6.
- Vieira-Sellaï L, Quintana M, Diop O, Mercier O, Tarrit S, Raimi N, et al. Green HPLC quantification method of lamivudine, zidovudine and nevirapine with identification of related substances in tablets. Green Chem Lett Rev 2022;15(3):695-704.
- Makita-Chingombe F, Ocque AJ, DiFrancesco R, Maponga C, Muzambi F, Monera-Penduka TG, et al. Development and validation of a high performance liquid chromatography method to determine nevirapine in plasma in a resource-limited setting. Afr J Lab Med 2019;8(1):1-7.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]