- *Corresponding Author:
- D. A. Shah
Anand Pharmacy College, Opp. Town Hall, Anand-388 001, A. R. College of Pharmacy, P. Box No. 19, Vallabh Vidyanagar-388 120, India
E-mail: dimalgroup@yahoo.com
| Date of Submission | 28 November 2005 |
| Date of Revision | 02 March 2006 |
| Date of Acceptance | 20 December 2006 |
| Indian J Pharm Sci, 2006, 68 (6): 796-799 |
Abstract
A simple, specific, accurate and precise reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method was developed for the simultaneous determination of atorvastatin calcium and amlodipine besylate in tablet dosage forms. A phenomenex Luna C-18, 5 µm column having 250 × 4.6 mm i.d. in isocratic mode, with mobile phase containing methanol: acetonitrile: 50 mM KH2PO4 (20:50:30; pH 3.5) was used. The flow rate was 1.0 ml/min and effluent was monitored at 240 nm. The retention time of atorvastatin calcium and amlodipine besylate was 7.6 min and 3.2 min respectively. The linearity for atorvastatin calcium and amlodipine besylate was in the range of 5-120 µg/ml and 5-100 µg/ml respectively. The proposed method is accurate, precise, specific and rapid for simultaneous estimation of atorvastatin calcium and amlodipine besylate in tablets.
Atorvastatin calcium (ATV) is chemically [R-(R*,R*)]-2-(4-flurophenyl)-β,δ-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-[(phenylamino)carbonyl]-1H-pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid, calcium salt trihydrate [1,2]. Extractive spectrophotometry [3], HPLC [4-8], GC-MS [9], LC-MS [10], HPLC-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry [11–13] and HPTLC [14] methods have been reported for the estimation of atorvastatin calcium. While for estimation of atorvastatin calcium and aspirin combination, RP-HPLC [15] method has been reported. Amlodipine besylate (AML) is 3-ethyl-5-methyl (±)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-3,5-pyridine dicarboxylate, monobenzenesulphonate. Amlodipine besylate is official in British Pharmacopoeia [16]. Different high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods have been reported for the estimation of amlodipine in combination with other drugs [17-21] .
Atorvastatin calcium is an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3methyl glutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-Co A) reductase. This enzyme catalyses the conversion of HMG-Co A to mevalonate, an early and rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis [1,2]. Amlodipine besylate is a calcium channel blocker. It inhibits the trans-membrane influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscles and cardiac muscle [22]. The combination dosage forms of atorvastatin calcium and amlodipine besylate are available in the market for the treatment of hypertension, chronic stable angina, vasospastic angina, elevated serum triglyceride levels, primary dysbetalipoproteinemia. Present study involves development and validation of RP-HPLC method for the estimation of ATV and AML in combination dosage form.
A HPLC instrument (Shimadzu HPLC class VP series) with LC-10AT VP pump, variable wavelength programmable UV/VIS detector SPD- 10AVP, Phenomenex Luna C-18, 5 μm column having 250 × 4.6 mm i.d. was used. A Rheodyne injector with a 20 μl loop was used for the injection of sample. The combination tablet formulations containing atorvastatin calcium equivalent to atorvastatin 10 mg and 5 mg of amlodipine (Brand name Avas-AM, manufactured by Micro Laboratories Ltd., India and Starcad manufactured by Lupin Labs. Ltd., India) were procured from the local market. HPLC grade acetonitrile, methanol (E. Merck, India) and HPLC grade water (Milli-Q Water System) were used in this investigation. Orthophosphoric acid and KH2PO4 were of analytical reagent grade obtained from S.D. Fine Chemicals. Mobile phase was prepared by mixing 300 ml of 50 mM KH2PO4 with 500 ml of acetonitrile and 200 ml of methanol, and the pH was adjusted to 3.5 using orthophosphoric acid. The solution was filtered using Whatman filter paper (No. 1) and sonicated for 10 min and then used.
Standard stock solutions were prepared by weighing pure ATV and AML (25 mg each) separately and dissolving in 25 ml volumetric flask, and volume was made up to the mark with methanol. Both the solutions were filtered through Whatman filter paper (No. 1) and further diluted to obtain final concentration of 100 μg/ml each. Calibration curves were prepared by taking appropriate aliquots of standard ATV and AML stock solutions in different 10 ml volumetric flasks and diluted up to the mark with mobile phase to obtain final concentrations of 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 120 μg/ml of ATV and 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 μg/ml of AML respectively. Standard solutions (n = 6) were injected through 20 μl loop system, and chromatograms were obtained using 1.0 ml/min flow rate. The effluent was monitored at 240 nm. Calibration curve was constructed by plotting average peak area against concentration, and regression equation was computed.
Twenty tablets were weighed accurately and finely powdered. Tablet powder equivalent to 10 mg ATV (and 6.70 mg of AML) was taken in 50 ml volumetric flask and the volume made up to the mark with methanol. Further 1 ml of this solution was diluted to 10 ml with mobile phase to obtain final concentration of ATV 20 μg/ml and AML 13.4 μg/ml. The solution was filtered using Whatman filter paper (No. 1), and it was sonicated for 10 min. Sample solutions were chromatographed (n = 3), and concentrations of ATV and AML in tablet samples were found using regression equation.
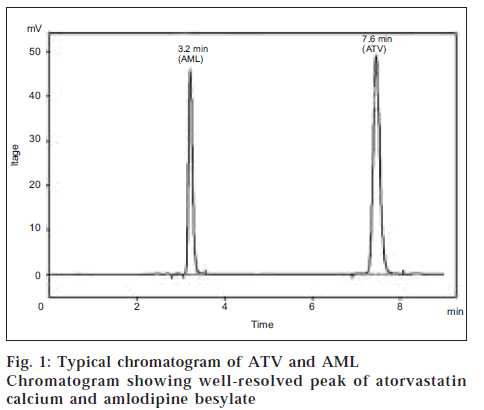
Both the drugs are soluble in methanol. Different combinations of solvents were tried in order to separate them from mixed standards. Different mobile phases were tried - like methanol: acetonitrile (80:20), methanol: acetonitrile: water (45:45:10), methanol: acetonitrile: water (75:10:15). Satisfactory separation was obtained with the mobile phase methanol: acetonitrile: 50 mM KH2PO4 (20:50:30; pH 3.5). The retention time of ATV was found to be 7.6 min, and that of AML was found to be 3.2 min (fig. 1). The detection of ATV and AML was carried out at 240 nm as their UV spectra shows appreciable absorbance at this wavelength. The regression equation obtained for ATV was Y = 25.29x + 1.53 (r = 0.9990) in the concentration range of 5-120 μg/ml; and for AML, Y = 22.63x - 4.25 (r = 0.9994) in the concentration range of 5-100 μg/ml. The correlation coefficient value shows that the method is linear.
System suitability tests were carried out as per USP XXIV [23] on freshly prepared standard stock solutions of ATV and AML, and parameters obtained are summarized (Table 1). Intra- and Inter-day precision studies were carried out, and results show that the method is reproducible. Limit of detection and limit of quantification were found to be 0.13 μg/ml and 0.32 μg/ml for ATV respectively and 0.09 μg/ml and 0.2 μg/ml for AML respectively (Table 1). The results obtained by the proposed method were close to the label claim of both the drugs (Table 2). The low value of standard deviation indicates that the method is accurate. To study the accuracy of the proposed method, recovery experiments were carried out. A fixed amount of pre-analyzed sample was taken and standard drug was added at three different concentrations. The values of percentage recovery show that the proposed method is accurate (Table 3). The proposed method is accurate, precise, repeatable and reproducible and can be used for routine analysis of ATV and AML in combination tablets.
| Parameters | AT V | AML |
|---|---|---|
| Retention time (min) | 7.6 | 3.2 |
| Asymmetry (n=5) | 1.29 | 1.49 |
| Resolution (n=5) | 18 | |
| Theoretical plates (n=5) | 10736 | 5125 |
| Calibration range | 5 – 120 mg/ml | 5 – 100 mg/ml |
| Limit of detection | 0.13 mg/ml | 0.09 mg/ml |
| Limit of quantification | 0.32 mg/ml | 0.2 mg/ml |
Different validation and system suitability parameters of proposed method
Table 1: Validation And System Suitability Parameters
| Formulation | Labeled amount (mg) | Amount found (mg)* | % of drug found ± SD* | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT V | AML | AT V | AML | AT V | AML | |||
| Tablet 1 | 10.34 | 6.93 | 10.28 | 6.85 | 99.42 ± 0.93 | 98.84 ± 0.94 | ||
| Tablet 2 | 10.34 | 6.93 | 10.25 | 6.88 | 99.13 ± 0.91 | 99.28 ± 0.87 | ||
*Mean value ± standard deviation of three determinations; Tablet 1 is Avas AM, manufactured by Micro Laboratories Ltd., India; and Tablet 2 is Starcad, manufactured by Lupin Labs. Ltd., India, both containing atorvastatin calcium equivalent to atorvastatin 10 mg and 5 mg of amlodipine, ATV is atorvastatin calcium and AML is amlodipine besylate
Table 2: Analysis Of Atv And Aml In Tablets
| Amount of sample taken (µg/ml) | Amount of standard drug added (µg/ml) | Amount of drug recovered (µg/ml) | % drug recovered | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT V | AML | AT V | AML | AT V | AML | AT V | AML |
| 20 | 13.4 | 0 | 0 | 19.67 | 13.62 | 98.35 | 101.64 |
| 20 | 13.4 | 0 | 0 | 19.87 | 13.38 | 99.35 | 99.85 |
| 20 | 13.4 | 0 | 0 | 20.08 | 13.29 | 100.40 | 99.18 |
| 20 | 13.4 | 10 | 7 | 29.70 | 20.47 | 99.00 | 100.34 |
| 20 | 13.4 | 10 | 7 | 29.79 | 20.32 | 99.30 | 99.61 |
| 20 | 13.4 | 10 | 7 | 29.45 | 20.20 | 98.17 | 99.02 |
| 20 | 13.4 | 20 | 15 | 39.47 | 28.47 | 98.67 | 100.25 |
| 20 | 13.4 | 20 | 15 | 39.71 | 28.27 | 99.27 | 99.54 |
| 20 | 13.4 | 20 | 15 | 39.84 | 28.12 | 99.60 | 99.01 |
| 20 | 13.4 | 30 | 20 | 49.46 | 33.55 | 98.92 | 100.45 |
| 20 | 13.4 | 30 | 20 | 49.70 | 33.24 | 99.40 | 99.52 |
| 20 | 13.4 | 30 | 20 | 49.94 | 33.11 | 99.88 | 99.13 |
ATV -Aatorvastatin calcium, AML -Amlodipine besylate
Table 3: Recovery Study Of Atv And Aml
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Tejal R. Gandhi, Principal, Anand Pharmacy College, Anand, for providing necessary facilities and encouragement. The authors are also thankful to M/s Blue Cross Labs. Ltd., Mumbai, for providing gift sample of atorvastatin calcium; and to M/s Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Ahmedabad, for providing gift sample of amlodipine besylate.
References
- Budavari, S., Eds., In; The Merck Index, 12th Edn., Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse station, NJ, 1996, 897.
- Gennaro, A. E., Eds., In; Remington’s-The Science and Practice of Pharmacy, 20th Edn., Vol. II, Mack Publishing Co., Easton, PA, 2000, 1294.
- Erk, N., Anal. Lett., 2003, 36, 2699.
- Muls, E., De Baeker, G., Brohet, C. and Heller, F., Acta Cardiol., 2001, 56, 109.
- Verd, J. C., Peris, C., Alergret, M., Diaz C., Hernandez, Z. G. and Sanchez, R. M., Brit. J. Pharmacol., 1999, 127, 1479.
- Bleske, B. E., Willis, R. A., Anthony, M., Casselberry, N., Datwani, M., Uhley, V. E., Secontine, S.G. and Shea, M. J., Amer. Heart J., 2001, 142, 262.
- Altuntas, T. G. and Erk, N., J. Liq. Chromat. Technol., 2004, 27, 83.
- Erturk, S., Aktas, E. S., Ersoy, L. and Ficicioglu, S., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2003, 33, 1017.
- McKenney, J. M., McCormick, L. S., Weiss, S., Koren, M., Kafonek, S. and Blanck, D. M., Amer. J. Med., 1998, 104, 137.
- Black, A, E., Sinz, M. W., Hayes, R. N. and Woolf, T. F., Drug Metab. Dispos., 1998, 26, 755.
- Miao, X. S. and Metcalfe, C. D., J. Chromat., 2003, 998, 133.
- Jemal, M., Ouyang, Z., Chen, B. C. and Teitz, D., Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 1999, 13, 1003.
- Bullen, W. W., Miller, R. A. and Hayes, R. N., J. Amer. Soc. Mass Spectrom., 1999, 10, 55.
- Yadav, S. S., Mhaske, D. V., Kakad, A. B., Patil B. D., Kadam, S. S. and Dhaneshwar S. R., Indian J. Pharm. Sci., 2005, 67, 182.
- Manoj, K., Shanmugapandiyan, P. and Anbazhagan, S., Indian Drugs, 2004, 41, 284.
- British Pharmacopoeia Vol. I, The H. M. Stationery Office, U.K., 2002, 117.
- Goweri, N., Vaidyhyalingam, V. and Shanta, A., Indian Drugs, 2002, 39, 532.
- Rao, J. R., Kadam, S. S. and Mahadik, K. R., Indian Drugs, 2002, 39, 378.
- Kadam, S. S., Mahadik, K. R., Agarawal, H. and Kaul, N., Int. Pharm. Fed. World Cong., 2002, 62, 38.
- Dhorda, U. J. and Shekar, N. B., Indian Drugs, 1999, 36, 638.
- Argekar, A. P. and Powar, S. G., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2000, 21, 1137.
- O’Nell, M. J., Eds., In; The Merck Index, 13th Edn., Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ, 2001, 86.
- The United States Pharmacopoeia, XXIV, National Formulary, XIX, US Pharmacopoeial Convention, Inc., Rockville MD., 2000, 1923.