- *Corresponding Author:
- P. Huang School of Public Health, Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi 330000, China E-mail: huangpengncu@163.com
| This article was originally published in a special issue, “Therapeutic Perspectives in Biomedical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences and their Nursing Methods” |
| Indian J Pharm Sci 2021:83(4)spl issue “15-21” |
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms
Abstract
To explore the correlation between 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T gene polymorphism and autism susceptibility and to provide the evidence-based medicine for the prevention and treatment of autism. The retrieval database includes the VIP Chinese Science and Technology journal database, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang database, PubMed, Wiley online library and Web of science. Chinese retrieval form: “Autism” and “methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase”. English retrieval form: “methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase”) and (“autism” or “autism spectrum disorders”) and (“C677T” or “polymorphism” or “genotype”). The retrieved time was till June 30, 2020 and the languages were limited to Chinese or English. Stata 12.0 software was used for meta-analysis, the evaluation indexes including heterogeneity test, merged effect, sensitivity analysis and publication bias evaluation. Based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 11 articles were included in the analysis. The meta-analysis shows that T/C allele odds ratio=0.56 (p<0.001), indicating that the T allele of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T may be an Autism spectrum disorder risk factor. The odds ratio of genotype CT vs. CC was 1.44 (p<0.001), the odds ratio of genotype TT vs. CC was 3.05 (p<0.001), the odds ratio of genotype TT+CT vs. CC was 1.81 (p<0.001), the odds ratio of genotype TT vs. CT+CC was 2.52 (p<0.001). CT, TT and TT+CT genotypes were positively correlated with autism susceptibility, indicating that CT, TT and TT+CT genotypes may increase the risk of autism susceptibility. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T gene polymorphism has a positive correlation with autism susceptibility.
Keywords
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T gene polymorphism, autism susceptibility, metaanalysis
Autism was a kind of pervasive developmental disorder disease, also known as infantile autism or autism disorder [1-3]. Its main clinical manifestations were social communication disorder, communication disorder and rigid. In 2018, a survey by the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showed that the prevalence of autism was about 1 % and most of them were children [4]. Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) was a common manifestation of autism. It was reported that the prevalence of ASD among children in the United States can reach 2 % and the boys were more likely to suffer from the disease than girls [5]. In China, the prevalence of ASD among children has also reached about 0.5 % and the proportion of boys and girls was about 5:1 [6]. Thus it can be seen that the prevalence rate of ASD was high and most of them were boys. However, its pathogenesis was not very clear and most of the studies think that it was related to the synergistic effect of heredity, environment, autoimmune function, oxidative stress, inflammatory biomarkers [7-9]. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) [10] was a metabolic enzyme that plays a key role in the folate metabolism, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation and DNA synthesis and repair. Folate-methionine metabolism was abnormal in patients with ASD, thus MTHFR gene polymorphism may be associated with ASD. Some studies have pointed out that the frequency of MTHFR gene mutation in ASD patients is significantly higher than that in healthy patients [11,12] and some studies focus on Chinese children, suggesting that MTHFR gene mutation may be a genetic risk factor for ASD in children [13]. Due to the small sample size of single study, inconsistent examination methods and confounding factors, the results of different studies are inconsistent. At present, single study is not enough to clarify the relationship between MTHFR gene polymorphism and ASD genetic susceptibility. However, the foreign meta-analysis of MTHFR gene polymorphism and ASD has not been included in domestic literature due to the analysis of multiple MTHFR gene polymorphisms. Therefore, this study collected relevant literature at home and abroad and conducted a meta-analysis on the relationship between MTHFR (C677T) gene polymorphism and ASD, so as to provide reference for the clinical prevention and treatment of ASD in children.
Data and Methods
Inclusion criteria:
The case-control study on the relationship between the MTHFR C677T gene polymorphism and autism susceptibility published at home and abroad with autism patients as the case group and the people with no autism as the control group; the frequency of genotypes or alleles in the case group and the control group was studied; the repeatedly published literature was included in the study with larger sample size; a standardized gene polymorphism detection technique was used.
Exclusion criteria:
Repetitive literature; systematic review of literature; review of literature, book chapter literature; genotype data were not reported or described clearly.
Literature retrieves:
The retrieval database includes the VIP Chinese Science and Technology journal database (VIP), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang database (Wanfang Data), PubMed, Wiley online library and Web of science. Chinese retrieval form: “Autism” and “MTHFR”. English retrieval form: (“MTHFR” or “methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase”) and (“autism” or “ASD”) and (“C677T” or “polymorphism” or “genotype”). The retrieved time was till June 30, 2020 and the languages were limited to Chinese or English.
Data extraction:
The literature screening and data extraction were carried out independently by two researchers and the extraction contents of each study were as follows, the first author, the year of publication, the sample size, the method of genotype detection, the number of cases in the case group and the control group and the frequency of genotypes and alleles in the case group and the control group.
Statistical treatment:
Stata 12.0 software was used for meta-analysis. Five genotypes (T vs. C, CT vs. CC, TT vs. CC, TT+CT vs. CC and TT vs. CT+CC) were selected to calculate the merging effect value odds ratio (OR) and 95 % confidence interval (CI) to estimate the association between MTHFR (C677T) gene polymorphism and ASD. Q test and I2 heterogeneity were used to evaluate the qualitative and quantitative heterogeneity of the included study. If p>0.1 or I2<50 %, choose the fixed effect model, otherwise choose the random effect model. Sensitivity analysis was used to explore stability of consolidated results. The Begg’s method and Egger’s method was used for testing publication bias.
Discussion
Literature retrieval:
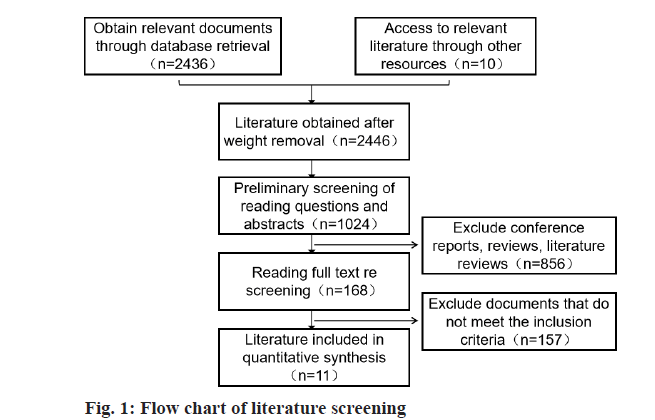
After literature retrieval, a total of 168 related literatures were obtained, including 34 Chinese literatures, 134 English literatures. And 68 repetitive literatures, 83 reviews of literatures and book chapters and 6 literatures with incomplete data were removed. Finally, a total of 11 qualified literatures were included [11-21]. Flow chart of literature screening is shown in fig. 1.
The basic characteristics of the inclusion research:
A total of 2795 cases were included and divided into the experimental group (n=1211) and the control group (n=1584). The distribution frequency of gene polymorphism in each group was consistent with Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium (HWE). The number and proportion of different genotypes in the experimental group were CC (505, 41.7 %), CT (497, 41.0 %), TT (209, 17.3 %, respectively. In the control group, the number and proportion of different genotypes were CC (806, 50.9 %), CT (602, 38.0 %), TT (176, 11.1 %), respectively. As shown in Table 1.
.| Author, year | Cases | Frequency of C677 genotype (Cases, experimental group/control group) | C677 allele (experimental group/control group) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | Control group | TT | CT | CC | TT+CT | CT+CC | C | T | |
| Liu 2011[11] | 205 | 384 | 39/41 | 98/166 | 68/177 | 137/207 | 166/343 | 234/520 | 176/248 |
| Guo 2012[12] | 186 | 186 | 30/16 | 77/83 | 79/87 | 107/99 | 156/170 | 235/257 | 137/115 |
| Zhao 2013[13] | 200 | 200 | 50/17 | 59/39 | 91/144 | 109/56 | 150/183 | 159/73 | 241/327 |
| Divyakolu 2013[14] | 50 | 50 | 0/0 | 8/22 | 42/27 | 8/22 | 50/49 | 76/92 | 24/8 |
| Shawky 2014[15] | 20 | 20 | 3/0 | 10/6 | 7/14 | 13/6 | 17/20 | 24/34 | 16/6 |
| Sener 2014[16] | 98 | 70 | 3/0 | 51/33 | 44/37 | 54/33 | 95/70 | 140/106 | 56/34 |
| Park 2014[17] | 251 | 425 | 37/80 | 136/204 | 76/139 | 173/284 | 212/343 | 265/408 | 204/310 |
| Meguid 2015[18] | 24 | 30 | 2/2 | 11/8 | 11/20 | 13/10 | 22/28 | 32/48 | 16/14 |
| Farida 2017[19] | 31 | 39 | 12/2 | 1/7 | 18/30 | 13/9 | 19/37 | 39/23 | 74/4 |
| Samira 2019[20] | 78 | 80 | 13/3 | 28/17 | 37/60 | 41/20 | 65/77 | 102/137 | 54/23 |
| Zhang 2020[21] | 68 | 100 | 20/12 | 18/17 | 30/71 | 38/19 | 48/88 | 78/159 | 58/41 |
Table 1: The Basic Characteristics of The Inclusion Research
Heterogeneity analysis:
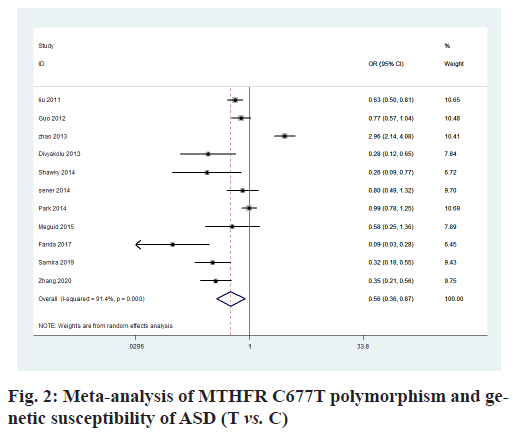
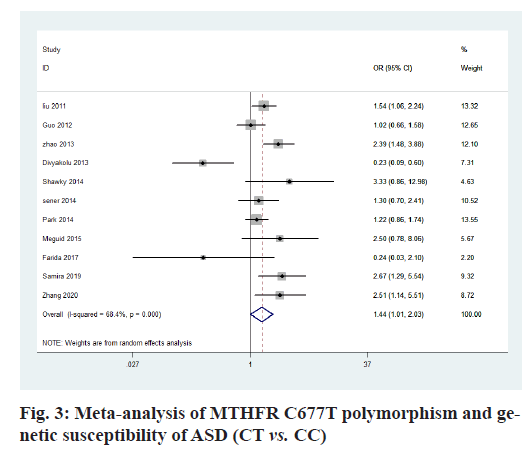
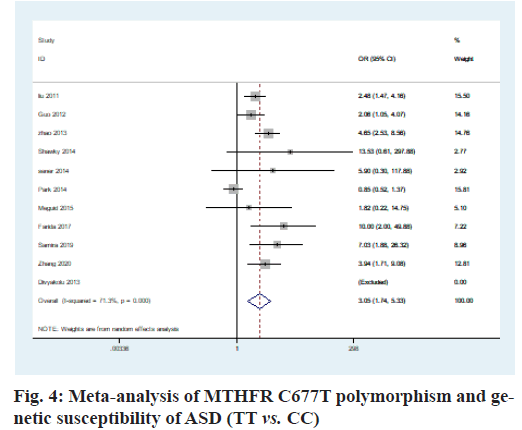
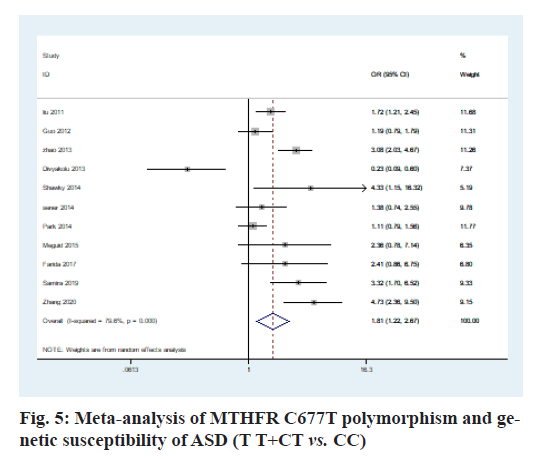
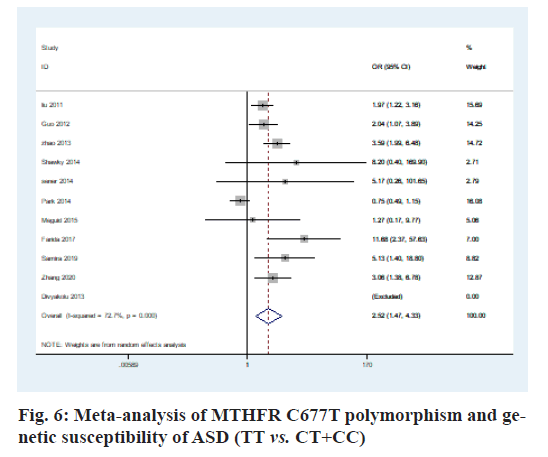
The heterogeneity analysis of the five genotypes at the MTHFR C677T locus showed that the heterogeneity of the five genotypes was large, so the random effect model was used. The results of meta-analysis showed that T allele might be a risk factor for ASD in T vs. C model (OR=0.56, 95 % CI=0.36-0.87, p<0.01) (fig. 2); CT genotype may be a risk factor for ASD in CT vs. CC model (OR=1.44, 95 % CI=1.01-2.03, p<0.001) (fig. 3); TT genotype may be a risk factor for ASD in TT vs. CC model (OR=3.05, 95 % CI=1.74-5.33, p<0.001) (fig. 4); TT+CT genotype may be a risk factor for ASD in TT+CT vs. CC model (OR=1.81, 95 % CI=1.22, 2.87, p<0.001) (fig. 5); TT genotype may be a risk factor for ASD in TT vs. CT+CC model (OR=2.52, 95 % CI=1.47-4.3, p<0.001) (fig. 6).
Cumulative meta-analysis:
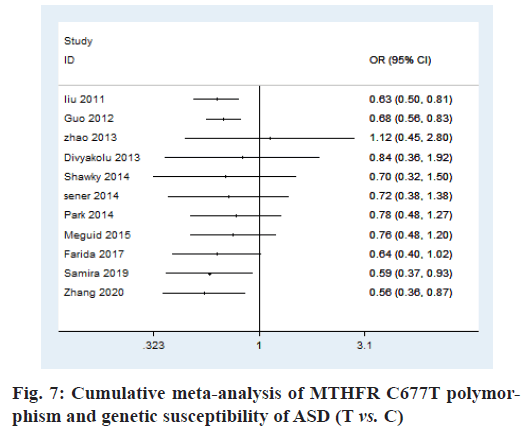
In order to investigate whether the conclusions are consistent, the cumulative meta-analysis was used. According to the cumulative meta-analysis of publication year, it is found that the research results are not completely consistent. The estimated value of OR and the CI tend to be stable and the changing trend is good. To make the experimental results more credible, the literature with larger samples should be used for this study (fig. 7).
Sensibility analysis:
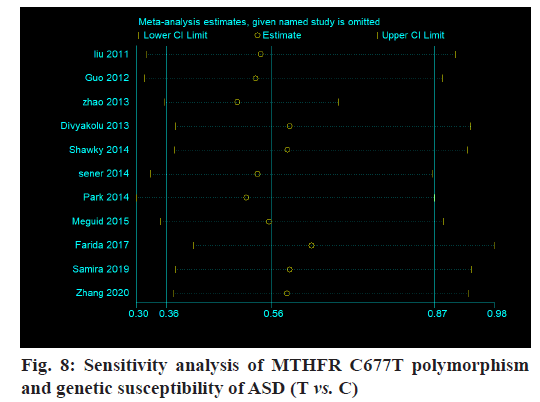
The sensitivity of this study is analyzed and the results show that there is no essential change in the combination of the fixed effect model and random effect model. At the same time, when any research results are excluded, the merger results do not change essentially, indicating that the results of this meta-analysis are stable (fig. 8).
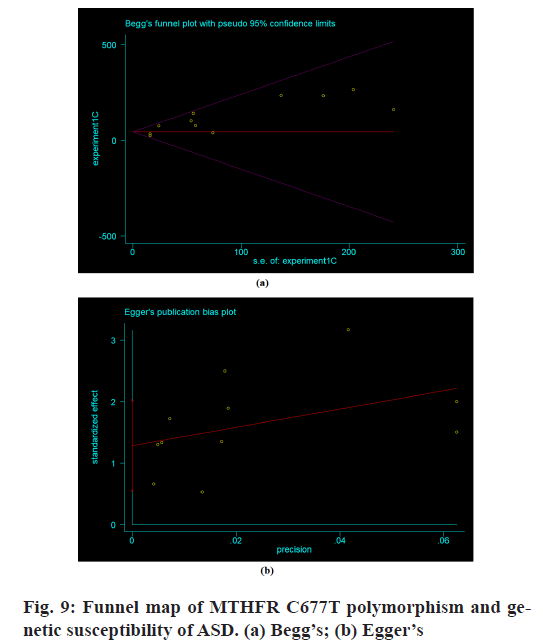
Publication bias:
The publication bias of the literature was analyzed by the Begg’s method and Egger’s method. Eleven studies were included. The publication bias was detected by Begg’s method and Egger’s method. The results of Begg’s method showed that p=0.076>0.05 and that of Egger’s method was p=0.254>0.05. The results showed that there was a certain bias in the literature publication (p>0.05) (fig. 9).
Previous studies have pointed out that autism was a neuropsychiatric disorder with brain dysplasia [22]. The incidence was increasing and it was a genetically heterogeneous disease with a heritability of 90 %. Its pathogenesis has always been the focus of researchon the treatment of autism. Most studies believe that the pathogenesis of autism may be related to the polygene regulation [23,24]. With the deepening of research, the research on genes related to autism susceptibility was becoming more and more abundant, but the conclusions were not uniform. There were many types of mutations in the human MTHFR gene. CT mutation at 677 locus was considered to be related to the occurrence of human diseases and related to the key enzyme that affects the occurrence of human diseases, MTHFR enzyme. MTHFR enzyme mainly converts N-5, N-10 methylenetetrahydrofolic acid to N-5-Methylenetetrahydrofolate (N-5-MTHF) and participates in the methionine cycle, which makes homocysteine re-methylation to methionine. CT mutation at 677 locus of the MTHFR gene can decrease the activity of MTHFR enzyme and affect the methylation of DNA [25], which can regulate the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells effectively and play a certain role in the normal function of the brain. For autism patients, the 677 CT mutation of the MTHFR gene may increase the risk of autism. Therefore, it is of great significance to further study the relationship between MTHFR gene 677 CT mutation and autism susceptibility from a genetic point of view.
There were many studies on the relationship between CT mutation at 677 loci of the MTHFR gene and autism susceptibility, but there were inconsistent conclusions. Divyakolu S [14] and Shawky RM [15] pointed out that the mutation rate of the MTHFR C677T gene in the case group was significantly higher than that in the control group, indicating that the MTHFR C677T gene was associated with autism susceptibility. However, some studies have pointed out that there was no correlation between the MTHFR C677T gene and autism susceptibility [26-28]. There were many reasons for the inconsistency of the research conclusions, which may be related to the selected research object, sample size, detection method. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct further research. In this paper, meta-analysis was used to study the relationship between the MTHFR C677T gene and autism susceptibility. It was found that the T/C allele OR=0.56 (p<0.001), indicating that T allele may be a risk factor for ASD. The OR of genotypic CT vs. CC was 1.44 (p<0.001, indicating that CT genotype may be a risk factor for ASD. The OR of genotype TT vs. CC was 3.05 (p<0.001), indicating that TT genotype may be a risk factor for ASD. The OR of genotype TT+CT vs. CC was 1.81 (p<0.001), indicating that TT+CT genotype may be a risk factor for ASD. The OR of genotype TT vs. CT+CC was 2.52 (p<0.001), indicating that TT genotype may be a risk factor for ASD. Generally speaking, CT, TT and TT+CT genotypes were positively correlated with autism susceptibility, indicating that CT, TT and TT+CT genotypes may increase the risk of autism susceptibility. The combination of fixed and random effect model distribution and the elimination of individual studies one by one for sensitivity analysis, there was no essential change in the results. Based on the analysis of the publication bias of the literature, the results show that the selected literature of this study has a certain publication bias and the publication bias is not large, indicating that the results of this study have strong stability.
Conclusion
To sum up, this study pointed out that there is a certain correlation between the MTHFR C677T gene and autism susceptibility. As the pathogenesis of autism was complex and affected by both environmental and genetic factors, it was limited to consider only the influence of single locus gene polymorphism in this study. At the same time, the selected sample size was insufficient and the environmental and polygene-related effects were not fully taken into account, which leads to some limitations in the conclusions of the study. Therefore, further research on the influence of large sample size and many factors are needed to further explore the relationship between the MTHFR C677T gene polymorphism and autism susceptibility.
Acknowledgements:
None
Conflicts of interest:
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
References
- Glessner JT, Wang K, Cai G, Korvatska O, Kim CE, Wood S, et al. Autism genome-wide copy number variation reveals ubiquitin and neuronal genes. Nature 2009;459:569-73.
- Bolton P, Macdonald H, Pickles A, Rios PA, Goode S, Crowson M, et al. A case‐control family history study of autism. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 1994;35(5):877-900.
- Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S, Skinner R, Martin J, Clubley E. The autism-spectrum quotient (AQ): Evidence from asperger syndrome/high-functioning autism, males and females, scientists and mathematicians. J Autism Dev Disord 2001;31(1):5-17.
- Lietz P, Kos J, Dix K, Trevitt J, Uljarevic M, O'Grady E. Protocol for a Systematic Review: Interventions for anxiety in school aged children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD): A mixed methods systematic review. Campbell Syst Rev 2018;14(1):1-48.
- Baio J. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders: Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 14 Sites, United States, 2008. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Morbidity & Mortality Weekly Report-Surveillance Summaries 2012;61:1-19.
- Wan Y, Hu Q, Li T, Jiang L, Du Y, Feng L, Wong JC, Li C. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders among children in China: a systematic review. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry 2013;25(2):70.
- Magnusson C, Rai D, Goodman A, Lundberg M, Idring S, Svensson A, et al. Migration and autism spectrum disorder: population-based study. Br J Psychiatry 2012;201(2):109-15.
- Gaigg SB, Cornell AS, Bird G. The psychophysiological mechanisms of alexithymia in autism spectrum disorder. Autism 2018;22(2):227-31.
- Doenyas C. Gut microbiota, inflammation and probiotics on neural development in autism spectrum disorder. Neuroscience 2018;374:271-86.
- Rosenblatt DS, Erbe RW. Methylenetetrahy drofolate reductase in cultured human cells. I. growth and metabolic studies. Pediatr Res 1977;11(11):1137-41.
- Liu X, Solehdin F, Cohen IL, Gonzalez MG, Jenkins EC, Lewis MS, et al. Population-and family-based studies associate the MTHFR gene with idiopathic autism in simplex families. J Autism Dev Disord 2011;41(7):938-44.
- Guo T, Chen H, Liu B, Ji W, Yang C. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphisms C677T and risk of autism in the Chinese Han population. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 2012;16(8):968-73.
- Zhao D, Sun CH, Yang XW. Association of MTHFR C677T and A1298C polymorphisms with childhood autism. Chin J Sch Health 2013;(1):52-5.
- Divyakolu S, Tejaswini Y, Thomas W, Thumoju S, Sreekanth VR, Vasavi M, et al. Evaluation of C677T polymorphism of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene in various neurological disorders. J Neurol Disord 2013.
- Shawky RM, El-baz F, Kamal TM, Elhossiny RM, Ahmed MA, El Nady GH. Study of genotype–phenotype correlation of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene polymorphisms in a sample of Egyptian autistic children. Egypt J Med Hum Genet 2014;15(4):335-41.
- Sener EF, Oztop DB, Ozkul Y. MTHFR gene C677T polymorphism in autism spectrum disorders. Genet Res Int 2014;2014.
- Park J, Ro M, Pyun JA, Nam M, Bang HJ, Yang JW, et al. MTHFR 1298A> C is a risk factor for autism spectrum disorder in the Korean population. Psychiatry Res 2014;215(1):258-9.
- Meguid N, Khalil R, Gebril O, El-Fishawy P. Evaluation of MTHFR genetic polymorphism as a risk factor in Egyptian autistic children and mothers. J Psychiatry 2015;18(1).
- El-baz F, Mohamed MA, Sadek AA, Othman AA. Study of the C677T and 1298AC polymorphic genotypes of MTHFR gene and phenotype genotype correlation in autism spectrum disorder. Sohag Med J 2017;21(1):1-10.
- Ismail S, Senna AA, Behiry EG, Ashaat EA, Zaki MS, Ashaat NA, et al. Study of C677T variant of methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase gene in autistic spectrum disorder Egyptian children. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2019;180(5):305-9.
- Zhang HC, Shang Q, Gao C. Association of MTHFR C677T and 5-HTTLPR gene polymorphisms with autism in Han children. J Clin Pathol 2020;7.
- Zhang Y, Liu Y, Huang H. Research progress in the etiology of autism. Chin J Gen Pract, 2017;20(11):1392-7.
- Yang Y, Jin ZJ, Wang J, Jin XM et al. Polymorphism of DLGAP1 gene in children with autism spectrum disorder. Chin J Pract Pediatr 2016;31(10):761-4.
- Zhang Y, Zeng J, Ke X, Qi Y, Lu JP. Expression recognition of autistic children and polymorphism of 5-HTLPR, 5-HT6, Neurexin and Neuroligin genes. Hebei Med J 2016;11(1):9-11.
- Liu WW, Dong XZ, Liu P. MTHFR 677 C/T polymorphism-new ideas about depressive disorder treatment. Chin Pharmacol Bull 2015;10(7):915-9.
- Dos Santos PA, Longo D, Brandalize AP, Schuler-Faccini L. MTHFR C677T is not a risk factor for autism spectrum disorders in South Brazil. Psychiatr Genet 2010;20(4):187-9.
- Schmidt RJ, Hansen RL, Hartiala J, Allayee H, Schmidt LC, Tancredi DJ, et al. Prenatal vitamins, one-carbon metabolism gene variants and risk for autism. Epidemiology 2011;22(4):476-85.
- Pasca SP, Dronca E, Kaucsar T, Craciun EC, Endreffy E, Ferencz BK, et al. One carbon metabolism disturbances and the C677T MTHFR gene polymorphism in children with autism spectrum disorders. J Cell Mol Med 2009;13(10):4229-38.