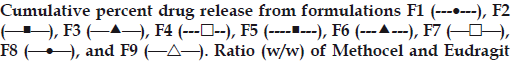- *Corresponding Author:
- R. Jalil
Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Dhaka, Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh
E-mail: raju1559@yahoo.com
| Date of Submission | 28 July 2008 |
| Date of Revision | 20 March 2009 |
| Date of Acceptance | 15 May 2009 |
| Indian J Pharm Sci 2009, 71 (3): 252-258 |
Abstract
The aim of the present study was the determination of formulation factors and the in vitro evaluation of an extended release dosage form of a freely soluble weakly basic drug (alfuzosin hydrochloride). Binary mixer of one hydrophilic polymer (hydroxypropylmethylcellulose) and one directly compressible Eudragit (RS PO) was used in tablets prepared by direct compression. The amounts of both polymers were taken as independent variables for the 3 2 Factorial design. The percent drug releases at 1, 6, 12 and 20 h were selected as responses. The main effect and interaction terms were quantitatively evaluated using mathematical model. Dissolution data were fitted to zero order, first order, and Higuchi's release kinetics to evaluate kinetic data. Both the diffusion and erosion mechanisms were responsible for drug release as shown by the power law. The release of Alfuzosin was prolonged for 20 h by binary mixer indicating the usefulness of the formulations for once daily dosage forms.
Keywords
Alfuzosin hydrochloride, Eudragit RS PO, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, matrix tablet, release kinetics
Alfuzosin hydrochloride, a selective alpha adrenergic antagonist is used against benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) [1-3] in elderly males. The prostate gland of the patients enlarges in BPH and prevents urine flow from bladder which results in urinary retention. The treatments available are surgical removal of excess tissue or drug therapy [4]. Two classes of drugs are used, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and alpha adrenergic antagonists. The second class includes terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin and alfuzosin.
Alfuzosin is freely soluble in water [5-6], and thus readily absorbed after administration. The oral absorption is significantly aided by the presence of food. The dose of immediate release alfuzosin tablet is 2.5 mg thrice daily [7-9]. Recently 10 mg once daily extended release formulation has become available in the market [10] which is more convenient for older patients [11]. Marketed alfuzosin formulation is a three layered Geomatrix tablet that requires special facilities, high cost, more time and complex operation than conventional formulations [12]. An easier directly compressible formulation was reported by Nair et al. [13] which is also followed in the current experiment.
As the drug is recently introduced, the data regarding the formulation and drug excipients compatibility are inadequate. Low viscosity hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) was used by Nair et al. [13] to prepare controlled release alfuzosin tablet (10 mg) that sustained drug release only for 12 h. To obtain once daily dosage form, high viscosity HPMC (such as Methocel K15M) should be used which can sustain for longer period. For freely soluble drugs like alfuzosin, a large quantity of HPMC is required to control the release that ultimately results in tablets which are difficult to swallow. This problem can be resolved by using water insoluble polymer in the formulation. Therefore, directly compressible Eudragit (RS PO) was used in present study along with Methocel K15M. Similar binary mixer was reported by several workers [14-16] who used different grades of HPMC and Eudragit for preparing matrix tablets.
HPMC is widely used in matrix formulations as a release retardant polymer [17-19] that controls drug release by quickly forming a gel barrier. When a drug is formulated with gel forming hydrocolloids such as HPMC, it swells in the gastric fluid affording a prolonged gastric residence time. On the other hand, water insoluble Eudragit RS is ammoniomethacrylate copolymer (Type B) made with copolymers of acrylate and methacrylates with quarternary ammonium group. The ammonium groups are present as salts and make the polymers permeable. The objective of the study was to investigate how high viscosity HPMC and directly compressible Eudragit combination affect the dissolution rate of alfuzosin from matrices and to study the qualitative effect of fillers on drug dissolution.
Materials and Methods
The following materials were used in the experiment: Alfuzosin HCl BP (Standard Chem. and Pharma Co. Ltd, Taiwan), microcrystalline cellulose PH 101 (MCC; Ming Tai Chemical Co. Ltd., Taiwan), high viscosity HPMC (Methocel K15M CR, The Dow Chemical Company, USA), Eudragit RS PO (Rohm GmbH, Germany), magnesium stearate (Paul Lohman, Germany), lactose (Flowlac, Meggle GmbH, Germany) and dibasic calcium phosphate (Interpharm ltd., UK). Other chemicals used were reagent grade.
Experimental Design
A 32 full factorial design was adopted for the experiment where two variables (X1, X2) were the amount of the two release controlling polymers as shown in Table 1. The selected responses for all possible 9 formulations were percent of drug release at 1, 6, 12 and 20 h. Methocel K15M was evaluated at 30, 40 and 50% while Eudragit RS PO was evaluated at 20, 30 and 40%.
| Formulation code | Weight (mg)/ Tablet | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfuzosin HCl | Methocel K15 MCR | Eudragit RS PO | Magnesium Stearate | MCC 101 | Total | |
| F1 | 10 | 150 | 60 | 3 | 77 | 300 |
| F2 | 10 | 90 | 120 | 3 | 77 | 300 |
| F3 | 10 | 90 | 90 | 3 | 107 | 300 |
| F4 | 10 | 150 | 90 | 3 | 47 | 300 |
| F5 | 10 | 120 | 120 | 3 | 47 | 300 |
| F6 | 10 | 150 | 120 | 3 | 17 | 300 |
| F7 | 10 | 120 | 60 | 3 | 107 | 300 |
| F8 | 10 | 120 | 90 | 3 | 77 | 300 |
| F9 | 10 | 90 | 60 | 3 | 137 | 300 |
Table 1: Composition of Tablet Formulations.
Preparation of Matrix tablets
Tablets were fabricated by direct compression according to the formula given in Table 1. The amount of active ingredient and tablet weight was held constant. All ingredients except lubricant were sieved through # 40 mesh and mixed manually for 10 min. Magnesium stearate (1%) was then added after passing through # 60 mesh and the powder mixture was blended for 2 min. The tablets were compressed with B type 16 station rotary compression machine (Manesty, UK) using 10 mm diameter punches with 1.5 ton compression force.
Physical Evaluation of Tablets
Hardness was determined using a Monsanto hardness tester while friability was determined according to British Pharmacopoeia with a Roche friabilator (Erweka, Germany). Bulk density and tapped density of the powder blend was determined with graduated cylinders according to USP guidelines. Hausner ratio and Carr’s index was determined to assess the flow property and compressibility of the powder blend [20].
In vitro dissolution studies
Dissolution studies were carried out for extended release Alfuzosin formulations using 0.01N HCl as dissolution medium [21]. The amount of drug dissolved in the medium was determined by UV spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan) at 244 nm wavelength. Dissolution studies were conducted by USP method 2 at 100 rpm [21] and the temperature was maintained at 37±0.5o. As the tablets have floating tendency, metallic sinker was used to keep tablets immersed into the medium.
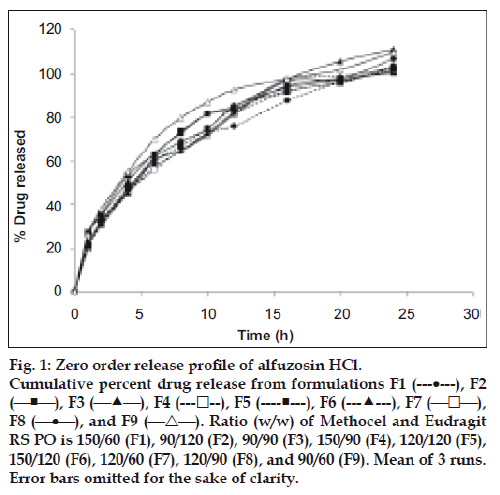
This operation was continued for 24 h while samples of 5 ml were withdrawn at regular interval from the dissolution medium and replaced with fresh dissolution medium to maintain the volume constant. The samples were filtered and suitably diluted. Drug dissolved at specified time periods was plotted as mean percent release versus time (h) curve (fig. 1). This drug release profile was fitted into several mathematical models to get an insight of the release mechanism of the drug from the dosage form.
Drug Release Kinetics
The rate of drug release from the preparation may follow zero order kinetics, first order kinetics or Higuchi’s model. To evaluate the mechanism of drug release from the preparation, data of drug release may be plotted in Korsmeyer et al’s equation [22], Log (Mt/ Mf) = Log k+nLogt, which is often used to describe the drug release behavior from polymeric systems, where Mt is the amount of drug release at time t, Mf is the amount of drug release after infinite time; k is a release rate constant incorporating structural and geometric characteristics of the dosage form, n is the diffusional exponent indicative of the mechanism of drug release [23].
The log value of percent drug dissolved is plotted against log time for each formulation according to the equation. For a cylinder shaped matrix the value of n ≤ 0.45 indicates Fickian (case I) release; > 0.45 but < 0.89 for non-Fickian (anomalous) release; and > 0.89 indicates super case II type of release. Case II generally refers to the erosion of the polymer and anomalous transport (Non-Fickian) refers to a combination of both diffusion and erosion controlled drug release [24].
Mean Dissolution Time (MDT) can be calculated from dissolution data according to Mockel and Lippold [25] equation to characterize the drug release rate from the dosage form and the retarding efficiency of the polymer. MDT value can be calculated from dissolution data using the equation MDT = (n/n+1) k-1/n, where n is the release exponent and k is release rate constant.
A higher value of MDT indicates a higher drug retaining ability of the polymer and vice-versa. Similarity factor (f2) is the measurement of similarity of two different dissolution curves. When f2 value is greater than 50, the curves are similar. The value is determined by the equation f2= 50log [{1+(1/n) Σ(Rt- Tt)2}-0.5.100] ,where n is the number of dissolution sample times, and Rt and Tt are the individual percentages dissolved at each time point t for the reference and test dissolution profiles respectively [26].
Statistical analysis
The response surface graphs and multiple regression analysis were carried out by Design Expert 7.0 (Stat- Ease Inc., Minneapolis, Minnesota) software at 5% significance level.
Stability study
Stability study of selected formulations was tested according to International Conference of Harmonization guideline. The tablets were stored in Alu-Alu blister for 3 mo in stability chamber (Memmert, Germany) at 40°/75% RH. After 3 mo, tablets were tested for drug content and in vitro dissolution.
Results and Discussion
The weight variation of the tablets ranged between 0.13-3.0% (1.25±0.39%), thickness between 4.2-4.5 mm (4.35±0.03 mm) and hardness was within 0.5- 2.15 kg/cm2 (1.14±0.18 kg/cm2) as shown in Table 2. The hardness of the tablets increased proportionally with the amount of Methocel K15M due the binding property of HPMC. The weight variation and friability of the batches complied with British Pharmacopoeia. The tablets were prepared by direct compression method, therefore the particle size and flow property of the powder blend should be in acceptable range. The particle size was on an average 420 μm and flow property was determined by Hausner ratio (1.37-1.42) and Carr’s Index (27.14%-29.58%). The data proved that the flow properties and compressibility of blends were satisfactory [20]. Thus all the physical parameters of different batches were within control.
| Code | Weight variation % | Hardness (Kg/cm2) | Friability % |
Bulk density (loose) g/cm2 | Bulk density (tapped) g/cm2 | Carr's index | Hausner ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.25 | 2.15 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 28.57 | 1.4 |
| F2 | 3 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.71 | 28.17 | 1.39 |
| F3 | 3 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.71 | 28.17 | 1.39 |
| F4 | 0.16 | 2 | 0.01 | 0.52 | 0.72 | 27.78 | 1.38 |
| F5 | 1.28 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.7 | 27.14 | 1.37 |
| F6 | 0.13 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 28.57 | 1.4 |
| F7 | 2 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 28.57 | 1.4 |
| F8 | 1 | 0.8 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 0.71 | 29.58 | 1.42 |
| F9 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.72 | 29.17 | 1.41 |
Table 2: Physical Characteristics of Tablets.
About 25% of drug was released within 1st h (t25%= 1.11±0.23 h, mean±SD) of in vitro dissolution. It took 4-5 h to release about 50% of drug (t50% = 4.59 ±0.6 h, mean±SD) and 75% drug released within 10 h (t75% =10.56±0.94 h, mean±S.D.) from all formulations (Table 3, fig. 1). The highest release retardant formulations were 150/60,150/90 and 120/60 Methocel-Eudragit (w/w) ratio as determined by their MDT values. The gradual increase of the acrylic polymer did not affect the drug release rate as indicated by f2 calculation. Among Methocel- Eudragit w/w ratio of 90/60, 90/90 and 90/120, the first formulation was taken as reference (Rt). The data indicates up to 40% Eudragit is not sufficient for reducing release of freely soluble drug like alfuzosin. On the other hand, when the Eudragit quantity was kept constant and HPMC level was increased, the drug release continued to fall. For instance, in Methocel-Eudragit w/w 90/60, 120/60 and 150/60 ratios the mean drug release after 12 h was 92.62, 81.59, and 76.12%, respectively.
| Kinetic parameters | Formulation code | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 | |
| Zero order | |||||||||
| r2 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.8 |
| K0 | 3.85 | 3.67 | 4.13 | 3.92 | 3.86 | 3.99 | 3.9 | 3.99 | 3.95 |
| First order | |||||||||
| r2 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| K1 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| Higuchi | |||||||||
| r2 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 |
| KH | 21.45 | 21.15 | 23.2 | 21.91 | 21.76 | 22.36 | 21.92 | 22.38 | 22.81 |
| Korsmeyer | |||||||||
| r2 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| n | 0.49 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 0.52 | 0.49 | 0.52 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.45 |
| K | 0.23 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.28 |
| MDT | 6.9 | 5.8 | 5.62 | 6.88 | 6.6 | 6.29 | 6.89 | 6.3 | 5.25 |
| t25% | 1.18 | 0.77 | 0.92 | 1.4 | 1.18 | 1.28 | 1.29 | 1.18 | 0.78 |
| t50% | 4.88 | 3.85 | 4.02 | 5.3 | 4.88 | 4.85 | 5.16 | 4.73 | 3.63 |
| t75% | 11.16 | 9.89 | 9.53 | 11.56 | 11.16 | 10.57 | 11.62 | 10.63 | 8.93 |
| t90% | 16.19 | 15.11 | 14.04 | 16.42 | 16.19 | 15.02 | 16.73 | 15.31 | 13.39 |
Table 3: Release Kinetics of Tablets.
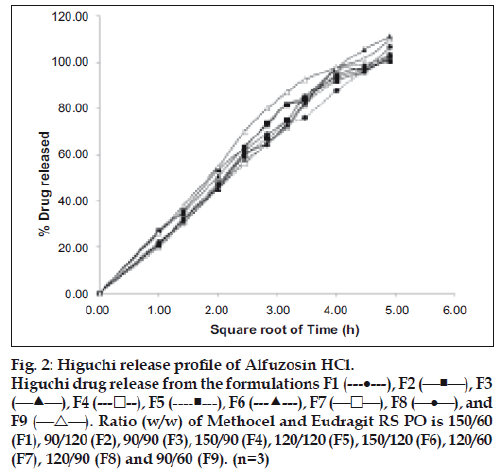
All the tablets showed good fit for Higuchi (r2=0.97- 0.99) and Korsmeyer (r2=0.98-0.99) kinetic models (Table 3; figs. 2 and 3). From Higuchi model it is evident that alfuzosin is released by diffusion process from the matrices. HPMC controls the release of soluble drugs by diffusion process and poorly soluble drugs by both diffusion and erosion mechanism [27-29]. This diffusion is probably due to the presence of gel barrier of HPMC. The diffusion exponent (n) of Korsmeyer model ranged from 0.43-0.52 indicating anomalous or non-Fickian transport. Therefore both diffusion and erosion mechanisms play role in alfuzosin release from Methocel-Eudragit matrix.
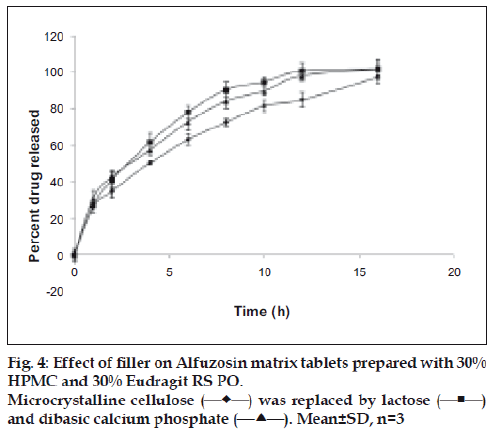
The tablets in the experiment were primarily prepared with microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) as filler. The effect of other fillers, such as directly compressible lactose and dibasic calcium phosphate dihydrate (DCP) on release of alfuzosin hydrochloride was also investigated. Lactose can act as a channeling agent due to its solubility while DCP can prevent water infiltration for its insoluble nature. Equal amounts of lactose or DCP replaced MCC in the formulations. Lactose containing tablets released alfuzosin faster than MCC and DCP as the release profiles of corresponding formulations were not similar (f2<50). Tablets containing DCP released slightly more drug than MCC containing formulation (fig. 4) as it tends to dissolve slowly in acidic media but the release profiles were not significantly different (f2>50).
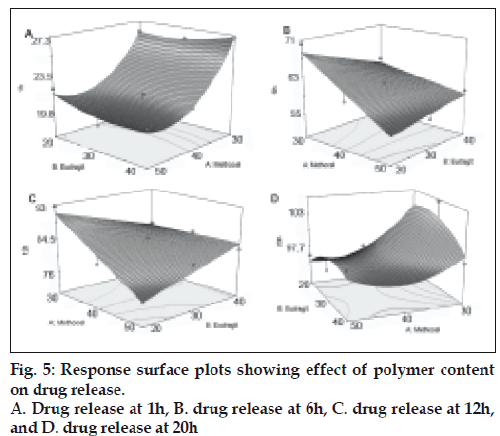
The drug release percentages at 1, 6, 12 and 20 h were selected as response variable (Table 4). These time periods are selected to detect any initial burst effect, time for 50% and 90% drug release. The equations of all responses (Table 5) represent the quantitative effect of independent variables upon the responses. A positive sign indicates a synergistic effect while a negative sign indicates antagonistic effect upon the responses [30]. b0 is the arithmetic mean response of the 9 runs and bi is the estimated coefficient for Xi (Table 5). It was found that Methocel (X2) was responsible for reducing drug release significantly (p<0.05) at 1, 6 and 12 h. Positive interaction between Methocel and Eudragit was found during 6 and 12 h (Table 5). Response surfaces depicting the effect of the casual factors on each response variable are presented in fig. 5.
| Formulation code | X1 | X2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | -1 | 1 | 22.23 | 57.2 | 76.12 | 96.29 |
| F2 | 1 | -1 | 27.05 | 63.13 | 83.69 | 97.9 |
| F3 | 0 | -1 | 26.25 | 63.56 | 85.21 | 105.66 |
| F4 | 0 | 1 | 19.88 | 56 | 81.9 | 96.26 |
| F5 | 1 | 0 | 21.42 | 59.94 | 84.12 | 95.85 |
| F6 | 1 | 1 | 20.88 | 59.67 | 82.46 | 99 |
| F7 | -1 | 0 | 21.09 | 59.99 | 81.59 | 97 |
| F8 | 0 | 0 | 21.65 | 61.5 | 85.11 | 97.54 |
| F9 | -1 | -1 | 26.18 | 70.14 | 92.62 | 101.85 |
Table 4: The Casual Factor and Responses of Model Formulations.
| Regression coefficient | Independent variables | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b0 | 21.02111 | 61.23667 | 83.64667 | - | |
| b1 | X1 | - | - | - | - |
| b2 | X2 | -2.74833 | -3.99333 | -3.50667 | |
| b12 | X1 X2 | - | 2.37 | 3.8175 | - |
| b11 | X1X1 | - | - | - | - |
| b22 | X2X2 | 2.358333 | - | - | - |
Table 5: Regression Equation for Each Response Variable Determined By Multiple Regression Analysis
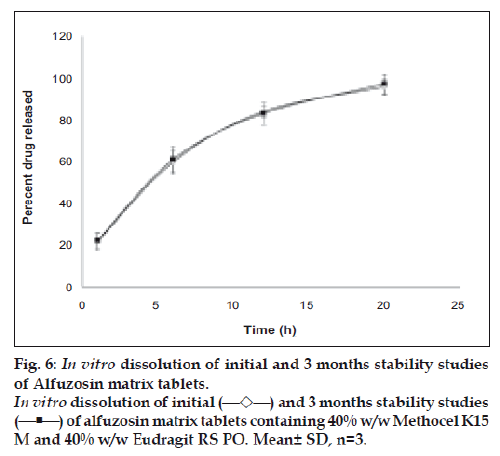
The physical, chemical and in vitro release of tablets kept at 40º/75% RH were studied according to previously mentioned methods revealed no significant change from initial values (fig. 6) which indicates the formulations were stable. Combination of two different polymers yielded tablets of acceptable physical characteristics and chemical stability. When used in combination, the role of HPMC in sustaining drug release is more prominent than Eudragit polymer and less amount of these polymers are required if MCC is used as a filler. In conclusion, stable extended release matrix tablets of alfuzosin can be prepared by adjusting the ratio of binary polymers and by selecting the suitable filler which can control drug release up to 20 h.
Acknowledgements
Authors like to thank Eskayef Bangladesh Ltd. (Former SmithKline & French, UK) for providing all materials and equipments required for the experiment.
References
- Guay DR (2004) Extended-release alfuzosin hydrochloride: A new alpha- adrenergic receptor antagonist for symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 2:14-23.
- Beduschi MC, Beduschi R, Oesterling JE. Alpha-blockade therapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia: From a nonselective to a more selective characteristics of diclofenac sodium. AAPS PharmSciTech 2003;4:43
- R, Shibata K, Horie K, Hirasawa A, Tsujimoto G. Use of recombinant a -adrenoreceptors to characterize subtype selectivity of drugs for the treatment of prostatic hypertrophy. Eur J Pharmacol 1995;288:201-7.
- Clayton LT, editor. Taber’s Cyclopedic medical dictionary. 18th ed. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers; 1998. p. 212.
- British Pharmacopoeia, Vol. I, London: Her Majesty’s Stationary Office, British Pharmacopoeia Commission; 2005. p. 73.
- Liu Q, Fassihi R. Zero-order delivery of a highly soluble, low dose drug alfuzosin hydrochloride via gastro-retentive system. Int J Pharm 2008;348:27-34.
- Jardin A, Bensadoun H, Delauche-Cavallier MC, Attali P. Long-term treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with alfuzosin: A 12-18 month assessment; BPHALF Group. Br J Urol 1993;72:615-20.
- Jardin A, Bensadoun H, Delauche-Cavallier MC, Stalla-Bourdillon A, Attali P. Long-term treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with alfuzosin: A 24-30 month survey, BPHALF group. Br J Urol 1994;74:579-84.
- Lukacs B, Grange JC, McCarthy C, Comet D. Clinical uroselectivity: A 3-year follow-up in general practice: BPA Group in General Practice. EurUrol 1998;33:28-33.
- Debruyne FMJ, Jardin A, Colloi D. Sustained-release alfuzosin, finasteride and the combination of both in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. EurUrol 1998;34:169–75.
- Kerrebroeck VP, Jardin A, Laval KU, Cangh VP. Efficacy and safety of a new prolonged release formulation of alfuzosin 10 mg once daily versus alfuzosin 2.5 mg thrice daily and placebo in patients with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. EurUrol 2000;37:306–13.
- Viswanathan NB, Ramakrishnan S, Raghuvanshi RS, Rampal A. Sustained release compositions containing Alfuzosin. US Patent 2003;20060147530.
- Nair A, Gupta R, Vasanti S. In vitro controlled release of Alfuzosin hydrochloride using HPMC-based matrix tablets and its comparison with marketed product. Pharm Dev Tech 2007;12:621-5.
- Takka S, Rajbhandari S, Sakr A. Effect of anionic polymers on the release of propranolol hydrochloride from matrix tablets. Eu J Pharm Biopharm 2001;52:75-82.
- Al-Taani BM, Tashtoush BM. Effect of Microenvironment pH of swellable and erodable buffered matrices on the release
- Gohel MC, Patel TP, Bariya SH. Studies in preparation and evaluation of pH-independent sustained-release matrix tablets of verapamil HCl using directly compressible eudragits. Pharm Dev Tech 2003;8:323-33.
- Colombo P. Swelling-controlled release in hydrogel matrices for oralroute. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 1993;11:37-57.
- Vyas SP, Jain NK, Khana S. Formulation and performance evaluation of controlled-release diclofenac sodium tablets. J Control Release 1989;10:219-23.
- Silvina AB, Maria CL, Claudio JS. In vitro studies of diclofenac sodium controlled-release from biopolymeric hydrophilic matrices. J Pharm PharmaceutSci 2002;5:213-9.
- Aulton ME, editor. Pharmaceutics, the science of dosage form design.Oxford: Churchill Livingstone; 2005. p. 133-4.
- Dissolution methods for drug products, US FDA. Available at: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/dissolution/dsp_SearchResults_Dissolutions.cfm?PrintAll=1. Accessed March 12, 2008.
- Ritger PL, Peppas NS. A simple equation for description of solute release II: Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. J Control Release 1987;5:37-42.
- Korsmeyer RW, Gurny R, Doelker E, Buri P, Peppas NA. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int J Pharm 1983;15:25-35.
- Siepmann J, Peppas NA. Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC).Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2001;48:139-57.
- Möckel J, Lippold BC. Zero-order drug release from hydrocolloid matrices. Pharm Res 1993;10:1066-70.
- United States Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for industry, dissolution testing of immediate release solid oral dosage forms; 1997.
- Mitchell K, Ford JL, Armstrong DJ, Elliott PN, Hogan JE, Rostron C. The influence of drugs on the properties of gels and swelling characteristics of matrices containing methylcellulose or hydroxypropylmethycellulose. Int J Pharm 1993;100:165-73.
- Katzhendler I, Hoffman A, Goldbergern A, Friedman M. Modeling of drug release from erodible tablets. J Pharm Sci 1997;86:110-5.
- Gao P, Nixon P, Skoug J. Diffusion in HPMC gels: II: Prediction of drug release rates from hydrophilic matrix extended-release dosage forms. Pharm Res 1995;12:965-71.
- Huang YB, Tsai YH, Yang WC, Chang JS, Wu PC. Optimization of sustained release propranolol dosage form using factorial design and response surface methodology. Biol Pharm Bull 2004;27:1626-9.