- *Corresponding Author:
- G. Sunitha
Gokaraju Rangaraju College of Pharmacy, Osmania University, Hyderabad-500 090, India
E-mail: g.sunitha88@gmail.com
| Date of Submission | 15 April 2013 |
| Date of Revision | 09 October 2013 |
| Date of Acceptance | 14 October 2013 |
| Indian J Pharm Sci, 2011, 73 (3): 300-302 |
Abstract
A simple and sensitive spectrofluorimetric method has been developed for the estimation of brimonidine tartrate in pure and eye drops. Linearity was obeyed in the range of 0.2-3.0 μg/ml in dimethyl formamide as solvent at an emission wavelength (lem) of 530 nm after excitation wavelength (lex) of 389 nm with good correlation coefficient of 0.998. The limit of detection and limit of quantification for this method were 22.0 and 72.0 ng/ml, respectively. The developed method was statistically validated as per International Conference on Harmonisation guidelines. The percentage relative standard deviation values were found to be less than 2 for accuracy and precision studies. The results obtained were in good agreement with the labelled amounts of the marketed formulations. The proposed method was effectively applied to routine quality control analysis of brimonidine tartrate in their eye drops.
Keywords
Brimonidine, Spectrofluorimetry, Validation
Brimonidine tartrate (BRT) chemically 5-bromo-6- (2-imidazolidinylideneamino) quinoxaline L-tartrate is a selective alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, used as ocular hypotensive agent [1,2]. Detailed literature survey revealed that few analytical methods are reported for quantification of BRT in eye drops and ophthalmic fluids by using spectrophotometry [3], high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [4-6], high performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) [7], UPLC [8] and liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy (LC/MS/MS) methods [9-11]. To the best of our knowledge, no method reported on the use of spectrofluorimetry for the quantification of BRT in eye drops. Spectrofluorimetry has assumed a major role in drug analysis because of its greater sensitivity and selectivity than absorption spectrophotometry [12-17]. Hence, we aimed to develop and validate a simple, precise, accurate, selective and high sensitive spectrofluorimetric method for the estimation of BRT in eye drops.
BRT pure drug was obtained as gift samples from Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd, Hyderabad, India. Eye drops (Alphagan-P and Alphagan) were procured from local pharmacies and dimethyl formamide (DMF) was purchased from Hi-Media, Mumbai, India. The fluorescence spectra and measurements were recorded using Shimadzu RF-5301 PC Spectrofluorophotometer, Shimadzu, Japan, equipped with 150 W Xenon arc lamp, 1 cm non-florescence quartz cell, connected to RFPC software.
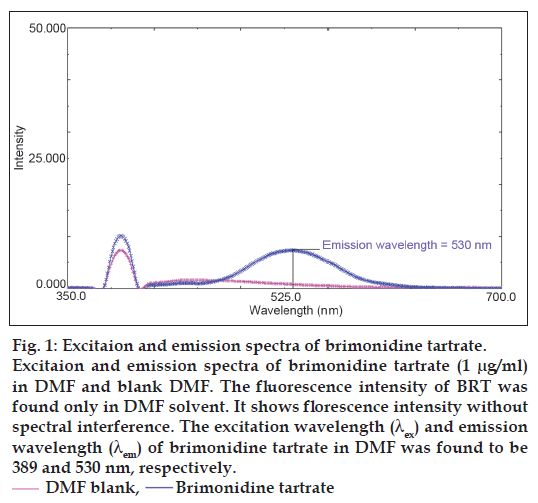
BRT molecule contains polycyclic aromatic systems like imidazole ring and quinoxaline ring, in which more π electrons are available to exhibit florescence. For spectrofluorimetric method purpose, various solvents were investigated such as acetonitrile, methanol, dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO), ethanol, DMF and different buffer systems. The fluorescence intensity of BRT was found only in DMF solvent. Hence, we selected DMF as solvent for quantification of BRT in eye drops at emission wavelength 530 nm after excitation wave length 389 nm as shown in fig. 1.
Figure 1: Excitaion and emission spectra of brimonidine tartrate. Excitaion and emission spectra of brimonidine tartrate (1 μg/ml) in DMF and blank DMF. The fluorescence intensity of BRT was found only in DMF solvent. It shows florescence intensity without spectral interference. The excitation wavelength (λex) and emission wavelength (λem) of brimonidine tartrate in DMF was found to be 389 and 530 nm, respectively. DMF blank, Brimonidine tartrate
The standard stock solution (1 mg/ml) BRT was prepared by transferring 10 mg of BRT in 10 ml volumetric flask and volume was made up to the mark with DMF. Aliquots of BRT stock solutions were taken into 10 ml volumetric flasks and diluted up to the mark with the solvent such that the final concentration of BRT was in the range of 0.2-3.0 μg/ml and analysed them by spectrofluorimeter with the proposed method. The calibration curve was constructed by plotting the analyte fluorescence intensity against the concentration (μg/ml). Calibration curve was evaluated by its correlation coefficient.
Optimum conditions of proposed method are mentioned in Table 1.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Excitation wavelength (nm) | 389 |
| Emission wavelength (nm) | 530 |
| Range (µg/ml) | 0.2-3.0 |
| Limit of detection (ng/ml) | 22.0 |
| Limit of quantification (ng/ml) | 72.0 |
| Correlation co-efficient (r2) | 0.998 |
| Slope (m) | 4.389 |
| Intercept ( c ) | 0.341 |
| Regression equation | Y=4.389x+0.341 |
Table 1: Optimum conditions of proposed method
For the assay of marketed formulations, 1 ml (Alphagan-p 0.15% and Alphagan 0.2%) of each containing 1.5 and 2 mg/ml of BRT were transferred into 10 ml volumetric flask and volume was made up to mark with DMF solvent to get the concentration 150 and 200 μg/ml of BRT, respectively. The solutions finally diluted with DMF to get concentrations within linearity range and intensity was measured by proposed method. Results were in good agreement with the label claim of the drug and are reported in Table 2. The proposed method validated according to International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines [18]. The percentage recoveries were found to be in the range of 98.8-102.4%. This indicates that the method is accurate. Results from precision expressed in terms of %RSD, found to be less than 2. No significant differences between intraday and interday precision, which indicated that the method is reproducible and reliable. The results of limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) revealed that proposed method was highly sensitive than previous methods.
| Formulation | BRT | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Label claim (mg/ml) | Amount found (mg, mean±SD, n=3) | % RSD | |
| Alphagan | 2.0 | 2.20±0.025 | 1.13 |
| Alphagan-p | 1.5 | 1.54±0.026 | 1.68 |
Table 2: Analysis of formulation
It is concluded that the proposed method was found to be simple, accurate, precise, specific and sensitive for the quantification of BRT in pure form and eye drops. The assay values were in good agreement with their respective labelled claim, which suggested no interference of formulation excipients in the estimation. The results obtained from validation proved that; the proposed method was scientifically sound. These advantages encourage that the proposed method can be routinely employed in quality control for analysis of BRT in eye drops.
References
- Sweetman SC, Martindale. The Complete Drug Reference. London:Pharmaceutical Press; 1999. p. 876.
- Maryadele JO. Neil. The Merck index, an encyclopedia of chemicals,drugs and biologicals. 14th ed. White House Station: Merck and Co.Inc; 2006. p. 1375.
- Prakash B, Pandurang D, Sarubh P, Sajeev C. Development andvalidation of stability indicating UV spectrophotometric method forthe estimation of brimonidine tartrate in pure form, formulation andpreformulation studies. Der Pharm Lett 2010;2:106-22.
- Mohan M, Ravi T. Method development and validation of brimonidinetartrate by high performance liquid chromatography. Asian J Res Chem2011;4:1591-4.
- Arun P, Senthil Kumar M, Mahadevan N. Simultaneous estimation ofbrimonidine tartrate and timolol maleate in nanoparticles formulationby RP-HPLC. Int J Recent Adv Pharm Res 2011;3:31-6.
- Narendra A, Deepika D, Mathrusri AM. Liquid chromatographic methodfor the analysis of brimonidine in ophthalmic formulations. E J Chem2012;9:1327-31.
- Mahajan A, Athensia F, Gandhi SV, Deshpande PB. Development andvalidation of high performance thin layer chromatographic methodfor estimation of brimonidine tartrate as bulk drug and in ophthalmicsolutions. Int J PharmTech Res 2010;2:1376-9.
- Manohar CS, Rajput AP. Development and validation of a new stabilityindicating analytical method for the determination of related compoundsof brimonidine tartrate in drug- substance and drug product usingUPLC. Int J Pharm Sci 2011;3:145-50.
- Madhavi A, Naidu A, Subbarao DV, Srinivas. Development andvalidation of a new LC-method for analysis of brimonidine tartrate andrelated compounds.Chromatographia 2009;69:1413-9.
- Andrew A, Diane D, Tang-liu S. Measurement of brimonidineconcentration in human plasma by a highly sensitive gaschromatography/mass spectrometric assay. J Pharm Biomed Anal1995;13:995-1002.
- Jiang S, Chappa SK, Prokseh JW. A rapid and sensitive LC/MS/MSassay for the quantitation of brimonidine in ocular fluids and tissues. JChromatogr B 2009;877:107-14.
- Fawzia I, Mohie KS, Manal I. Validated stability- indicatingspectrofluorimetric methods for the determination of ebastine inpharmaceutical preparations. Chem Cent J 2011;5:11.
- Mesut A, Emrah K. Validated spectrofluorimetric method for thedetermination of sunitinab malate, dyecomplexation approach for anovel anticancer drug. Acta Pharm Sci 2010;52:469-85.
- Mohamed W, Fathallah FB, Nahed ME. Synchronous fluorescencespectrofluorimetric method for the simultaneous determination ofmetaprolol and felodipine in combined pharmaceutical preparation.Chem Cent J 2011;5:70.
- El-Wasseef DR, El-Sherbiny DT, Abu-El-Enein MA.Simultaneousdetermination of labetalol and furosemide by first-derivativesynchronous spectrofluorimetry. J Floresec 2009;19:817-28.
- Belal F, El-Brashy A, El-Enany N, Tolba M. Conventional and firstderivative synchronous fluorometric determination of ethamsylate inpharmaceutical preparations and biological fluids, application to stabilitystudies. J Fluoresc 2011;21:1371-84.
- Panikumar AD, Sirisha N, Haripriya A, SatheshBabu R,Subrahmanyam CV. First derivative synchronous spectrofluorimetricquantification of telmisartan/amlodipine besylate combination in tablets.Dhaka Univ J Pharm Sci 2013;12:35-40.
- International Conference on Harmonization. Harmonized TripartiteGuideline, Validation of Analytical Procedures, Text and Methodology, Q2 (R1); 2005.