- *Corresponding Author:
- X. Zhu
Collaborative Innovation Center of Yangtze River Delta Region Green Pharmaceuticals, Zhejiang University of Technology, No.18 Chaowang Road, Hangzhou 310014, China
E-mail: zxy@zjut.edu.cn
| Date of Submission | 30 March 2017 |
| Date of Revision | 04 May 2018 |
| Date of Acceptance | 11 January 2019 |
| Indian J Pharm Sci 2019;81(2):211-218 |
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms
Abstract
Candesartan cilexetil was complexed with glycyrrhizic acid to enhance its aqueous solubility. Solid dispersion of candesartan cilexetil and glycyrrhizic acid were prepared by mechanochemical technique of milling at 120 rpm for 8 h. This solid dispersion could significantly improve the solubility of candesartan cilexetil in water. In vitro drug release showed a significant increase in drug dissolution rate after formation of a solid dispersion with glycyrrhizic acid. It was also found that the chemical stability of the solid dispersions was enhanced compared to pure candesartan cilexetil in a stability study involving heat, light, and long-term storage. The results of differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray powder diffraction shown that the drug existed in the amorphous state. Fourier-transform infrared spectra demonstrated that hydrogen bonding occurred between candesartan cilexetil and glycyrrhizic acid with mechanical and chemical treatment.
Keywords
Candesartan cilexetil, glycyrrhizic acid, mechanochemical technique, solubility, stability
Poorly water-soluble drugs often require higher dosage in order to reach the therapeutic plasma concentrations after oral administration. Improvement in the extent and rate of dissolution is highly desirable for such compounds, as this can lead to an increased and more reproducible oral bioavailability and subsequently to clinically relevant dose reduction and more reliable therapy [1]. A solid dispersion approach could increase the dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drugs thereby improve their bioavailability [2,3]. Usually, solid dispersions are two-component systems in which the drug is incorporated in the hydrophilic carrier. The drug within the hydrophilic carrier may be dispersed molecularly or occur as amorphous components [4].
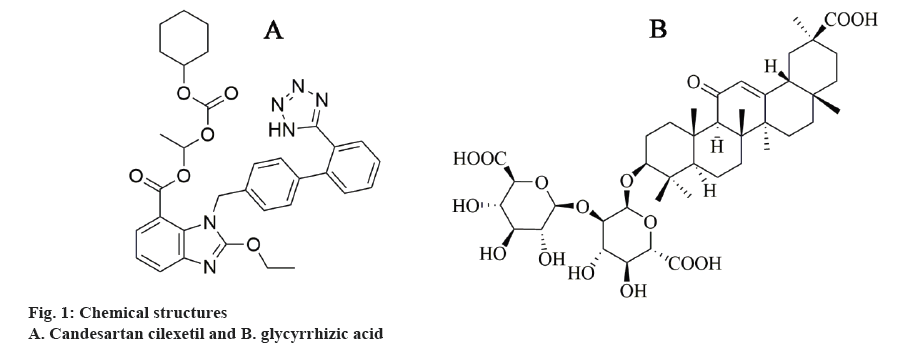
Candesartan cilexetil (Figure 1A), an inactive ester prodrug, is widely used to treat essential hypertension and heart failure [5]. During absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, it is rapidly and completely hydrolysed into candesartan, which is a highly potent and selective non-peptide angiotensin-II type-1 (AT1) receptor antagonist [6]. Candesartan cilexetil, as a new antagonist of AT1, has attracted greater attention of the antihypertensive drugs market [7]. However, the oral bioavailability of candesartan cilexetil (~15 %) is not as good as expected, mainly because of its poor water-solubility, efflux by drug resistance pumps in intestinal epithelial cells (P-glycoprotein), and first pass metabolism by cytochrome P450 3A4 [8,9]. Thus, several attempts were made to improve the dissolution rate and bioavailability of candesartan cilexetil, such as preparation of solid dispersions [10-12], cyclodextrins inclusion complexes [13], self-emulsifying drug delivery system [14], nanoparticles [15], or preparation of micelles [16]. Although much progress has been achieved through previous research, many formulations were normally prepared as liquids that is considered unfriendly to the environment and some formulations used large quantity of surfactants, which can induce gastrointestinal irritation.
In this study, solid dispersion of candesartan cilexetil were prepared employing the solid-state mechanochemistry, which has been found to be green, environment protecting, fast and an efficient process technology for pharmaceutical solid dispersion preparation [17,18]. Moreover, high fever, which could result by the use of a partial decomposed drug could be avoided [19]. Mechanochemical technology was widely used in terms of improving the water solubility of poorly soluble drugs, such as the preparation of solid dispersions, cyclodextrins inclusion complexes, eutectic and so on [20]. Recently, the use of mechanochemistry has become very attractive in the field of pharmaceutical industry to enhance the dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drugs [21]. In fact, compared with traditional “liquid phase” method, mechanochemical process offers significant advantages such as one-stage process, absence of solvents or melts and respective additional procedures, high strength of formed complexes and low operating costs [22,23]. Recent publications confirmed the prospectivity of mechanochemical approach on the examples of α-lipoic acid, simvastatin and other drugs [24-27].
Glycyrrhizic acid (GA, Figure 1B) is a good soluble natural saponin, extracted from liquorice roots, and widely applied as flavouring and sweetener. GA is a conjugate of two glucuronic acid molecules and a GA molecule and is capable of formation large micellelike aggregates in aqueous and water-alcohol solutions due to its amphiphilic properties [28]. Poorly watersoluble drugs can form solid dispersion with GA, which leads to increased solubility and therapeutic effect and, consequently, reduces the therapeutic doses of these drugs [29-31]. In addition, GA can increase the permeability of cell membranes for small molecules [32]. In the present investigation, a solid dispersion of candesartan cilexetil with GA was synthetized via ball milling. The complex formed was evaluated with X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and its dissolution behaviour. In addition, the stability of ball milling products regarding illumination and hyperthermia behaviour was investigated.
Materials and Methods
Candesartan cilexetil (purity ≥99 %) was obtained by Aladdin Industrial Corporation, China; GA was supplied by TCI Chemical Industry Co., Ltd, Shanghai, hina; PM-200 planetary ball mill (Retsch, Germany); HTY-EU802 rotating paddle apparatus (Tailin Bioengineering Equipments Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China); Waters 2695 Liquid chromatograph (Waters Corporation, USA).
Preparation of samples:
Candesartan cilexetil/GA solid dispersion was prepared in a planetary micro mill with stainless steel jars, which possessed 50 ml volume. Rotational speed of stainless steel jars is 120 rpm. Steel balls (diameter 12 mm) were used as grinding bodies. The duration of mechanical processing was from 0.5 to 16 h (0.5, 2, 4, 8, and 16 h). To prepare the solid dispersion, candesartan cilexetil/ GA mass ratio 1/5, 1/10, 1/20 and 1/50 was used. All the products should over 100 mesh sieve and preserved in a driers with a low temperature after sealed. Physical mixtures of candesartan cilexetil and GA were prepared by blending them in a small bottle.
Solubility study:
Solubility of samples was determined in water using a standardized shake bath method. The samples contained 30 mg candesartan cilexetil were placed in a HY-4 shaker-incubator (+37°, 200 rpm, Hangzhou Dewei Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. Hangzhou, China) for 48 h. The samples were then filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane filter and the filtrate was assayed per high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The test was parallel to the determination of three times.
HPLC analysis:
Waters 2695 HPLC system was used to determine the concentration of candesartan cilexetil. The HPLC system equipped with an UV detector set at 254 nm. Chromatographic analysis was performed on a reverse phase column (5 μm, 4.6×50 mm, Zorbax Eclipse XDB-C18) at ambient temperature. The mobile phase consisted of potassium dihydrogen phosphate buffer solution (pH 4.0) and acetonitrile (20:80, v/v). The flow rate was 1.0 ml/min and the injection volume was 5 μl for each sample. The calibration curve was rectilinear in the concentration range of 10-100 μg/ml with a correlation coefficient of 0.9999. The inter/ intraday accuracy and precision was within a relative standard deviation of ≤5 %.
Content test for candesartan cilexetil and its solid dispersions:
The co-milled products (containing 0.6 mg candesartan cilexetil) were weighed accurately by a BSA124S analytical balance (Sedorius, Germany). Then put them into different volumetric flasks with a capacity of 50 ml, respectively, and then added the ethanol into the volumetric flask as a solution until all components of complexes were completely dissolved. Added in ethanol up to the scale mark. The samples were suitably diluted and assayed by HPLC. The test replicates three times and calculates the percentage of practical and theoretical drug content in the grinding product (Table 1).
| Sample | Drug content, % from initial |
|---|---|
| Candesartan Cilexetil/GA (1:5, 8 H) | 98.8±1.07 |
| Candesartan Cilexetil/GA (1:10, 8 H) | 97.4±1.22 |
| Candesartan Cilexetil/GA (1:20, 8 H) | 99.5±0.98 |
| Candesartan Cilexetil/GA (1:50, 8 H) | 97.9±1.14 |
Table 1: Content Homogeneity
Same quality (~0.2 g) of candesartan cilexetil and the co-milled binary systems complexes (w/w=1:5,1:10 and 1:20 milling time 8 h) were divided into 3 equal portions. One was stored in a stability test chamber (DHG-9240A, Yiheng Scientific Instrument Co., LTD., Shanghai) under dry conditions at 60±0.5° to test the thermal stability of samples. The samples were taken out on day 5 and day 10, dissolved in ethanol and assayed using HPLC to calculate the contents of candesartan cilexetil.
Second portion was subjected to light stability test. The samples were kept in a photostability test chamber, whose light intensity was set at 4500±500 lux [33]. Samples were taken out and dissolved in ethanol, assayed using HPLC to calculate the contents of candesartan cilexetil at 5th and 10th d. The third portion was stored for 6 mo under room temperature in a sealed dryer, samples were taken out, dissolved in ethanol and assayed using HPLC to calculate the contents of candesartan cilexetil after 30, 90, 120 and 180 d.
In vitro dissolution test:
Determination of the dissolution rate in this study was according to method of the FDA [34]. The amount of milled products equivalent to 16 mg candesartan cilexetil and pure candesartan cilexetil were determined using a HTY-EU802 rotating paddle apparatus. Phosphate buffer of pH 6.7 was used as the dissolution medium (37±0.5°, 900 ml), and the paddle speed was set at 50 rpm. Five millilitre aliquots were withdrawn at 5, 10, 15, 30, 45 and 60 min, each time replacing the volume of sample with equal volume of preheated dissolution medium to maintain sink condition. The samples were filtered through 0.45 μm membrane filter and assayed for drug concentration using a HPLC method that was described earlier. Each dissolution rate test was repeated three times.
DSC analysis:
DSC thermograms were obtained under argon gas flow of 10 ml/min. Calibration of the DSC instrument (Instrument Scientific Specialists Inc., Omaha, NE, USA) was carried out using indium as a standard. Sample powders (5 to 7 mg) were crimped in an aluminium pan and heated at a rate of 10 K/min from 20° up to 250°.
XRD analysis:
Powder XRD was used to assess the degree of crystallinity of cogrinding products. XRD analysis was performed using an X'Pert PRO X-ray diffractometer (PA Analytical, Holland) with a CuKα radiation source at 40 kV voltage, 30 mA current and a scanning speed of 2 degrees/min from 0 to 60°.
FTIR analysis:
Infrared spectra of the samples were obtained using a Niclolet Avatar 370 instrument (Thermo Niclolet Corporation, USA). All samples were mixed with KBr for compressing into a thin tablet. The wave number of FTIR spectra ranged from 400 to 4000 cm−1 with a resolution of 2 cm−1.
SEM analysis:
Electron microscopic images were acquired using a Hitachi TM-1000 microscope (Tokyo, Japan). Samples were coated with gold using a Jeol JFC-1600 auto fine coater (Tokyo, Japan). The coating parameters were as follows: sputtering time 30 s, amperage 30 mA, and film thickness 15 nm.
Results and Discussion
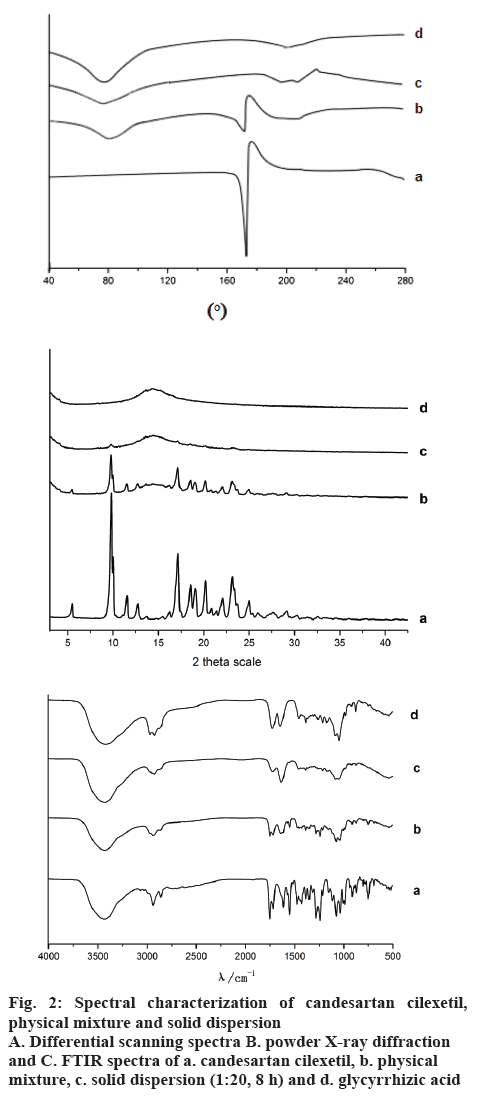
Thermal behaviours of candesartan cilexetil, a physical mixture of 1:20 candesartan cilexetil and GA, and the ball milled 1:20 solid complexes were shown in figure 2A. DSC thermogram of candesartan cilexetil showed a sharp endothermic peak at about 170°, which was the result of the melting for candesartan cilexetil [13]. The thermogram of GA showed a very broad endothermic effect in the range from 70 to 100° due to release of water molecules. The characteristic melting endotherm peak appeared in the physical mixture of candesartan cilexetil and GA, but the complete disappearance of the candesartan cilexetil endothermic peak suggested that no crystal of candesartan cilexetil existed in GA solid dispersion.
The physical status of candesartan cilexetil in solid dispersion was further confirmed by XRD analysis (Figure 2B). Candesartan cilexetil showed the typical peaks at 2 θ values of 9.9, 17.26, 18.7, 19.62, 20.52, 23.14, and 25.16 degrees, indicating that candesartan cilexetil existed as crystalline form [13]. The characteristic peaks also existed in the physical mixture, which indicated that there was no interaction between drug and GA by the way of direct superposition. On the contrary, a broad peak without any drug crystalline peak was detected in the diffraction pattern of the mechanical activation complexes. The XRD data indicated that candesartan cilexetil was in the amorphous or molecular state in the mechanical activation solid dispersion, which accorded with the DSC measurements.
FTIR spectroscopy was used to investigate possible chemical reactions or H-bonding formation in the binary systems of candesartan cilexetil with GA. Pure candesartan cilexetil (Figure 2C) showed characteristic peaks ideal for candesartan cilexetil at 2942.83 cm−1 due to aromatic (−C-H) stretching, 2865.16 cm−1 for (O-H) stretching, 1751.99 cm−1 and 1716.92 cm−1 for ester (−C=O) stretching vibration, 1270.42 cm−1 and 1316.28 cm−1 due to (−C-O) stretching of carbonyl group of aromatic ester. It was found that the overall peaks were similar to the free GA in physical mixture. However, the C=O stretching vibration peak of candesartan cilexetil was still observed in the physical mixture indicating that there was no interaction between drug and GA. On the contrary, the C=O stretching vibration peak of candesartan cilexetil was completely disappeared in the milled complex of candesartan cilexetil/GA, probably indicating that the carbonyl group in candesartan cilexetil interacted with the hydroxyl group of GA.
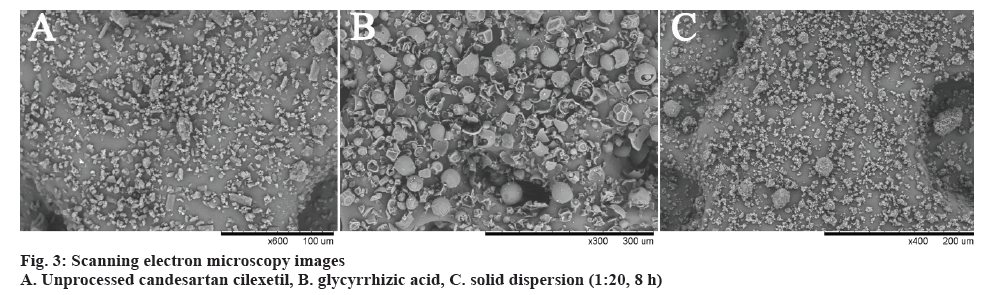
SEM images of the pure candesartan cilexetil, GA and corresponding solid dispersion in 1:20 mass ratio were shown in figure 3. Candesartan cilexetil demonstrated a slightly bacilliform crystallites within an irregular shaped particle. The morphological feature of GA was in the shape of spherical particle with different size. Emergence of the new morphological shape in solid dispersion compared to the pure drug and GA was indicative of the efficient formation of solid dispersion system. Moreover, according to SEM image of the solid dispersion, there were no observable drug particles on the surface of prepared solid dispersion, representing homogeneous distribution of the drug molecules in the solid dispersion system.
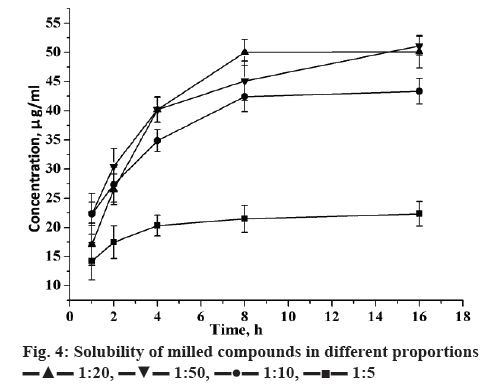
The solubility of candesartan cilexetil was enhanced with varied extent in formulation of mechanical-treated solid dispersions (Figure 4). In addition, the contents of candesartan cilexetil in solid dispersion were all nearly 100 % from theoretically calculated. It indicated that during mechanical treatment, there was no significant destruction and loss of candesartan cilexetil in solid dispersions. The increase of GA amount increased candesartan cilexetil solubility. As an amphiphilic carrier, GA can promote drug micellar solubilisation. The micelle formation occurs when the GA concentration is above its critical micellar concentration. Additionally, the solubility of candesartan cilexetil basically had no change when milled over 8 h. Therefore, 8 h was the best milling time for this system to prepare solid dispersions with good solubility of drug.
The dissolution of coground mixtures and candesartan cilexetil were shown in figure 5. Dissolution from unprocessed candesartan cilexetil order kinetics with a very slow dissolution rate (≈1 % in 60 min). Compared to pure drug, the dissolution rate of 1:5 and 1:10 (w/w) compounds has increased significantly, reached to 50.2 and 75.4 % in 60 min, respectively. Moreover, the candesartan cilexetil approximation acquired a complete release in 60 min when the ratio of candesartan cilexetil and GA has reached to 1:20. The mechanochemically obtained compositions have the most improved dissolution profile may be attributed to the decrease in the drug crystallinity during the preparation process. The improved dissolution rate of candesartan cilexetil in the physical mixture might be attributed to the hydrophilic nature of GA, which can increase the dissolution rate by reduction in the interfacial tension between the poorly-soluble drug and the release medium.
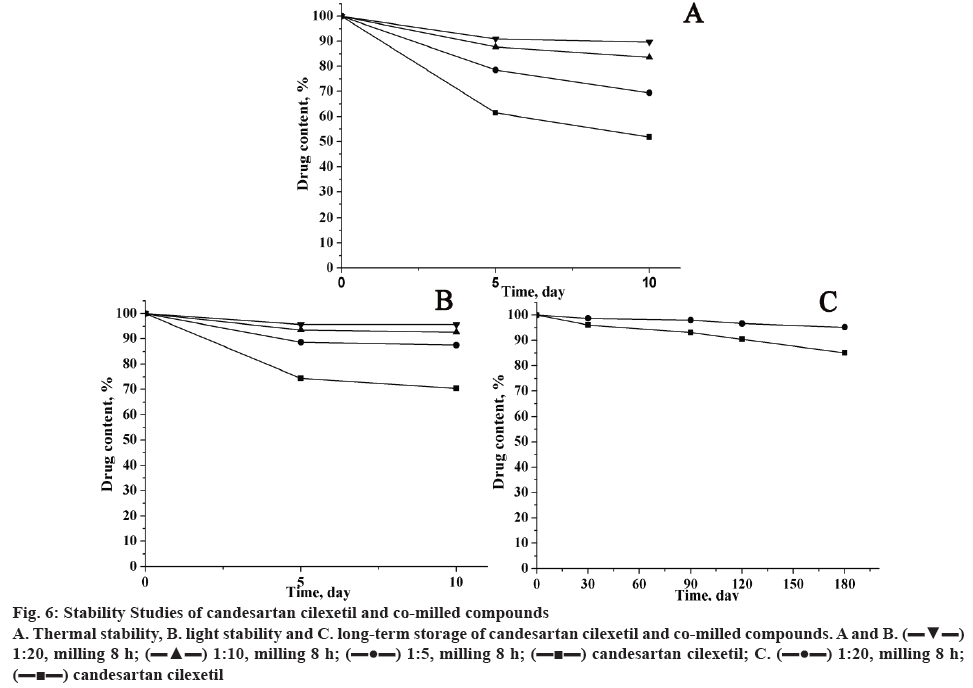
The stability tests of pure candesartan cilexetil and its mechanochemically obtained complexes were carried out at high temperature, light irradiation and long-time storage, and results of drug content were represented in figure 6. It was found that the content of candesartan cilexetil in all samples decreased with the extended storage time. For mechanochemically obtained solid dispersions, the drug content was higher than pure candesartan cilexetil, which suggested the stability of solid dispersion has an enhanced stability. In addition, the proportion of candesartan cilexetil and GA has a great effect for the stability of the compounds.
Figure 6: Stability Studies of candesartan cilexetil and co-milled compounds
A. Thermal stability, B. light stability and C. long-term storage of candesartan cilexetil and co-milled compounds. A and B.  1:20, milling 8 h;
1:20, milling 8 h;  1:10, milling 8 h;
1:10, milling 8 h;  1:5, milling 8 h;
1:5, milling 8 h;  candesartan cilexetil; C.
candesartan cilexetil; C.  1:20, milling 8 h;
1:20, milling 8 h;  candesartan cilexetil
candesartan cilexetil
In this study, mechanochemical milling process that allows getting final product in one technological step without using of any organic solvents has been applied to prepare solid dispersions of candesartan cilexetil with GA. Formation of the solid dispersions was proved by XRD, FTIR and DSC analysis. In vitro drug release showed a significant increase in drug’s dissolution rate after formation a solid dispersion with GA. On the other hand, the stability assay showed that the chemical stability of solid dispersions had an enhanced compared with pure candesartan cilexetil. In conclusion, solid state mechanochemical milling process could be a most useful method for the preparation of complexes of candesartan cilexetil with GA, which are promising to improve the oral bioavailability of candesartan cilexetil and might be considered for development of the lowdose drug market. This study still has some limitation. In stability study, we only calculate the drug content, without using other determination methods. In next studies, it is better to use drug content determination combined with FTIR, DSC and NMR to investigate the stability, which makes the results more convincing.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
References
- Eloy JO, Marchetti JM. Solid dispersions containing ursolic acid in Poloxamer 407 and PEG 6000: Acomparative study of fusion and solvent methods. Powder Technol 2014;253:98-106.
- Chaudhari SP, Dugar RP. Application of surfactants in solid dispersion technology for improving solubility of poorly water soluble drugs. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec 2017;41:68-77.
- Leuner C, Dressman J. Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2000;50(1):47-60.
- Gurunath S, Kumar SP, Basavaraj NK, Patil PA. Amorphous solid dispersion method for improving oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. J Pharm Res 2016;6:476-80.
- McClellan KJ, Goa KL. Candesartan cilexetil. Drugs 1998;56:847-69.
- Gao F, Zhang Z, Bu H, Huang Y, Gao Z, Shen J, et al. Nanoemulsion improves the oral absorption of candesartan cilexetil in rats: performance and mechanism. J Control Release 2011;149:168-74.
- Aylin G, Nuray Y, Ayla Ç. Trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles enhances dissolution of the poorly water soluble drug candesartan-cilexetil. Macromol Res 2010;18:986-91.
- Surampalli G, KN B, Patil PA. Corroboration of naringin effects on the intestinal absorption and pharmacokinetic behavior of candesartan cilexetil solid dispersions using in situ rat models. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 2014;41(7):1-9.
- Gurunath S, Nanjwade BK, Patil PA. Oral bioavailability and intestinal absorption of candesartan cilexetil: role of naringin as P-glycoprotein inhibitor. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 2015;41(1):170-6.
- Wang MR, Wang LZ. Preparation and dissolution of candesartan solid dispersion, stability study. Chin J Modern Appl Pharm 2011;28:654-8.
- Zhang HG, Fan CC, Zhu YN. Preparation of candesartan cilexetil immediate-release and sustained release solid dispersions. China Med Herald 2013;10:126-34.
- Pinto J, Leão AF, Riekes MK, França MT, Stulzer HK. HPMCAS as an effective precipitation inhibitor in amorphous solid dispersions of the poorly soluble drug candesartan cilexetil. Carbohydr Polym 2018;184:199-206.
- Al Omari AA, Al Omari MM, Badwan AA, Alsou'Od KA. Effect of cyclodextrins on the solubility and stability of candesartan cilexetil in solution and solid state. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2011;54(3):503-09.
- Aboulfotouh K, Allam AA, Elbadry M, Elsayed AM. Development and in vitro/in vivo performance of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems loaded with candesartan cilexetil. Eur J Pharm Sci 2017;109:503-13.
- Zhang Z, Gao F, Bu H, Xiao J, Li Y. Solid lipid nanoparticles loading candesartan cilexetil enhance oral bioavailability: in vitro characteristics and absorption mechanism in rats. Nanomedicine 2012;85:740-7.
- Satturwar P, Eddine MN, Ravenelle F, Leroux JC. pH-responsive polymeric micelles of poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(alkyl(meth)acrylate-co-methacrylic acid): Influence of the copolymer composition on self-assembling properties and release of candesartan cilexetil. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2007;65(3):379-87.
- Zhong L, Zhu XY, Luo XF, Su WK. Dissolution Properties and Physical Characterization of Telmisartan-Chitosan Solid Dispersions Prepared by Mechanochemical Activation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013;14(2):541-50.
- Barzegar-Jalali M, Valizadeh H, Shadbad MRS, Adibkia K, Mohammadi G, Farahani A. et al. Cogrinding as an approach to enhance dissolution rate of a poorly water-soluble drug (gliclazide). Powder Technol 2010;197:150-8.
- James SL, Adams CJ, Bolm C, Braga D, Collier P, Frišcic T, et al. Mechanochemistry: opportunities for new and cleaner synthesis. Chem Soc Rev 2012;41(1);413-47.
- Zhi HL, Samanta AK, Heng PWS. Overview of milling techniques for improving the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs. Asian J Pharm Sci 2015;10:255-74.
- Dushkin AV, Meteleva ES, Tolstikova TG. Mechanochemical preparation and pharmacological activities of water-soluble intermolecular complexes of arabinogalactan with medicinal agents. Russ Chem Bull 2008;57:1299-307.
- Mura P, Faucci MT, Parrini PL. Effects of grinding with microcrystalline cellulose and cyclodextrins on the ketoprofen physicochemical properties. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 2001;27(2):119-28.
- Dushkin AV, Meteleva ES, Tolstikova TG, Khvostov MV. Mechanochemical preparation and properties of water-soluble intermolecular complexes of polysaccharides and ß-cyclodextrin with pharmaceutical substances. Chem Sustain Dev 2010;18:631-40.
- Zheng M, Tang W, Kong R, Zhu X. Inclusion complex of a-lipoic acid containing alkalizer for improving the solubility and stability prepared by co-grinding. Indian J Pharm Sci 2017;79:544-52.
- Kong R, Zhu X, Meteleva E S, Chistyachenko YS, Suntsova LP, Polyakov NE, et al. Enhanced solubility and bioavailability of simvastatin by mechanochemically obtained complexes. Int J Pharm 2017;534(1-2):108-18.
- Chistyachenko YS, Dushkin AV, Tolstikova TG, Tolstikov GA, Lyakhov NZ, Polyakov NE, et al. Polysaccharide arabinogalactan from larch Larixsibirica as carrier for molecules of salicylic and acetylsalicylic acid: preparation, physicochemical and pharmacological study. Drug Deliv 2015;22:400-7.
- Prabhu P, Patravale V. Dissolution enhancement of atorvastatin calcium by cogrinding technique. Drug Deliv Transl Res 2016;6:380-91.
- Polyakov NE, Leshina TV. Glycyrrhizic acid as a novel drug delivery vector: synergy of drug transport and efficacy. Open Conf Proc J 2011;2:64-72.
- Dushkin AV, Tolstikova TG, Khvostov MV, Tolstikov GA. Complexes of polysaccharides and glycyrrhizic acid with drug molecules. Mechanochemical synthesis and pharmacological activity. In: Karunaratne DN, ed. The Complex World of Polysaccharides. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech; 2012. p. 573-602.
- Yang FH, Zhang Q, Liang QY, Wang SQ, Zhao BX, Wang YT, et al. Bioavailability enhancement of paclitaxel via a novel oral drug delivery system: paclitaxel-loaded glycyrrhizic acid micelles. Molecules 2015;20:4337-56.
- Dushkin AV, Meteleva ES, Tolstikova TG, Khvostov MV, Dolgikh MP. Complexing of pharmacons with glycyrrhizic acid as a route to the development of the preparations with enhanced efficiency. Chem Sustain Dev 2010;18:437-44.
- Selyutina OYu, Apanasenko IE, Polyakov NE. Membrane-modifying activity of glycyrrhizic acid. Russ Chem Bull 2015;64:1555-9.
- Frizon F, Mitsui ML, Marchetti JM. Dissolution rate enhancement of loratadine in polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 solid dispersions by solvent methods. Powder Technol 2013;235:532-9.
- Dangre P, Gilhotra R, Dhole S. Formulation and statistical optimization of self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of eprosartan mesylate for improvement of oral bioavailability. Drug Deliv Transl Res 2016;6(5):610-62.
 1:20, milling 8 h;
1:20, milling 8 h;  1:10, milling 8 h;
1:10, milling 8 h;  1:20 physical mixture,
1:20 physical mixture,  1:5, milling 8 h;
1:5, milling 8 h;  candesartan cilexetil
candesartan cilexetil