- *Corresponding Author:
- Shan Huang
Department of Electrocardiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui 230601, China
E-mail: hsff828052@163.com
| This article was originally published in a special issue, “Innovations in Biomedical Research and Drug Development” |
| Indian J Pharm Sci 2023:85(3) Spl Issue “186-191” |
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms
Abstract
In order to improve the therapeutic effect of breast cancer patients, trastuzumab combined with chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy was applied to breast cancer patients in this study and to observe the effect of this treatment on the abnormal rate of electrocardiogram and serum indexes of breast cancer patients. 60 patients received targeted therapy and chemotherapy during perioperative period. All patients received local radiotherapy after surgery. At the same time, for patients with poor peripheral blood vessels, jugular vein or subclavian vein catheterization should be performed before chemotherapy to avoid vein inflammation. The abnormal rate of electrocardiogram and serum indexes and rate of adverse reactions of 60 patients were examined. The results show that the abnormal electrocardiogram rate at T1, T2 and T3 was gradually increasing. The serum indexes after chemotherapy and radiotherapy are lower than those before chemotherapy and radiotherapy respectively. After chemotherapy and radiotherapy, there were 3 cases of radiation pneumonitis, 2 cases of pain and 2 cases of abnormal liver function. Postoperative chemotherapy and radiotherapy combined with trastuzumab can decrease serum levels in breast cancer patients. Meanwhile, the abnormal rate of electrocardiogram and cardiotoxicity were higher. Therefore, before trastuzumab therapy, cardiac function safety tests should be conducted in breast cancer patients and cardiac function should be closely monitored.
Keywords
Breast cancer, trastuzumab, chemotherapy and radiotherapy, electrocardiogram, serum indexes
Breast cancer belongs to female patients and is a malignant tumor caused by the proliferation of mammary epithelial cells. Clinical manifestations are usually irregular breast edge and hard unilateral breast, areola and skin will appear with large changes[1,2]. Since the mammary gland is not a vital organ, it is not actually fatal[3]. However, due to the lack of specific symptoms at the onset of the disease, early diagnosis is delayed and most diagnosed patients miss the best opportunity for surgical treatment due to the advanced stage. In addition, breast cancer cells lose their normal cellular characteristics and easy to shed. Once cancer cells fall off, free cancer cells will spread to the whole body with blood or lymph, endangering the life and health of patients[3-6]. As a result, breast cancer morbidity and mortality rates are currently high.
The traditional treatment for breast cancer is surgical excision. Although it can reduce the risk of deterioration, it can also affect body shape and reduce quality of life[7,8]. At present, there are mainly surgical treatment and adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. In recent years, most scholars have studied breast conserving therapy, mainly chemotherapy intervention[9-11]. Although certain effects can be achieved, but still cannot effectively improve the effect of intervention. Related studies show that overexpression of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) is more common in breast cancer patients. Under physiological conditions, HER2 can regulate the proliferation and differentiation of tissue cells but if there is abnormal activation of HER2, it will lead to tumor growth, recurrence and metastasis[12]. HER2 overexpression is found in 20 %-30 % of breast cancer patients, which often indicates poor prognosis[13]. Therefore, specific inhibition of the proliferation of HER2 overexpressed tumor cells is an important target for breast cancer treatment[14]. Lots of analysis has suggested that trastuzumab is a monoclonal antibody derived from recombinant Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)[15-17]. After entering the body, trastuzumab can inhibit growth factors specifically and improve the sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapy drugs, giving full play to the anti-tumor effects of drugs[18]. Trastuzumab, as a monoclonal antibody against HER2/neuprotooncogene (neu), can prevent human epidermal growth factor from adhering to HER2, thus blocking the growth of cancer cells. Because of its strong inhibitory effect and high safety, it is often used in the treatment of breast cancer with overexpression of HER2 at different stages. However, this drug has high cardiotoxicity, which further affects the therapeutic effect[19].
In order to improve the therapeutic effect of breast cancer patients, trastuzumab combined with chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy was applied to breast cancer patients in this study and to observe the effect of this treatment on the abnormal rate of Electrocardiogram (ECG) and serum indexes of breast cancer patients.
Materials and Methods
Clinical data:
A total of 60 female breast cancer patients admitted to our hospital from June 2016 to December 2022 were selected. The average age was 51.80±1.25 y. The average course of disease was 2.47±0.88 y.
Selection criteria:
Inclusion criteria: Meeting the diagnostic criteria for breast cancer[20]; confirmed by histopathology; patient data are complete; have the ability to read and write, can cooperate with the investigation and all patients signed informed consent.
Exclusion criteria: Allergic reaction to the drugs involved in this study; having mental illness and language difficulties; patients with complications of other serious diseases and genetic diseases; poor compliance, cannot cooperate with the completion of research and investigation; combined with other malignant tumors affect the quality of life; receiving other forms of treatment; pregnant and lactating women and severe insufficiency of heart, liver and kidney function.
Methods:
60 patients received targeted therapy and chemotherapy during perioperative period. All patients received local radiotherapy after surgery. At the same time, for patients with poor peripheral blood vessels, jugular vein or subclavian vein catheterization should be performed before chemotherapy to avoid vein inflammation. Chemotherapy is combined with gastric protection, antiemesis and leukemia treatment. For every 3 w one chemotherapy cycle was performed; imaging evaluation was performed for every 2-3 cycles of chemotherapy. All enrolled patients required adjuvant radiotherapy, which was completed within 6 mo after surgery and radiotherapy was performed after the exclusion of radiotherapy contraindications. Thoracic lymph nodes were treated with radiotherapy according to pathological stage. The patient was placed in supine position, with the upper limb of the affected side on the head and the upper limb of the healthy side on the body. The treatment site was simulated by Computed Tomography (CT) scan from the upper neck to the upper abdomen. Develop radiotherapy planning system with eclipse; normal heart tissue was mapped with Varian’s 23EX Clinac® linear accelerator. The lesion chest wall was compensated with 6 MV X-rays. The prescribed dose is 50 Gy 5 times every week; breast-conserving patients are usually treated with large-segment radiotherapy, prescribed dose is 39 Gy 5 times every week and the tumor bed was increased to 48 Gy. The 95 % isodose curve is required to rotate around the Planning Target Volume (PTV). The minimum dose point was 110 % of the prescribed dose. Keep the planned target area for dangerous organs within the standard limits. During treatment, if the patient has symptomatic Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), treatment is terminated when it is 15 % higher or lower than the normal lower limit (compared to baseline value).
Observation index:
The abnormal rate of ECG and serum indexes, and rate of adverse reactions of 60 patients were examined. The ECG of the two groups was detected before chemotherapy (T0), after 4 cycles of chemotherapy (T1), before radiotherapy (T2) and 2 mo after radiotherapy (T3), respectively. The patients were placed in the lying position under quiet state. 12-lead ECG was used for detection. Among them, sporadic premature beats, sinus bradycardia, borderline escape, left and right bundle branch block, incomplete left and right bundle branch block, atrioventricular block and ST-T abnormality were all ECG abnormalities. 5 ml of elbow venous blood was collected from the two groups at T0, T1, T2 and T3, respectively. Centrifuge at 3500 r/min for 10 min and collect serum. Then measure white blood cell count, neutrophil absolute value, hemoglobin and platelet count. The rate of adverse reactions (side effects) was recorded, including radiation pneumonitis, pain and abnormal liver function.
Results and Discussion
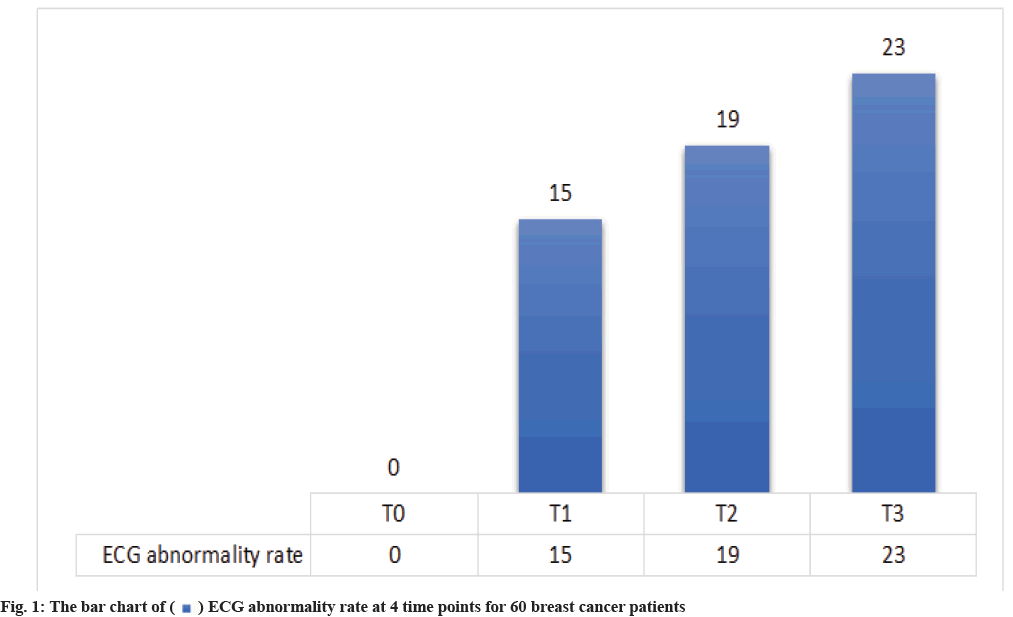
Abnormal ECG rate at 4 time points for 60 breast cancer patients were shown here. It can be seen from Table 1 and fig. 1 that the abnormal ECG rate at T1, T2 and T3 was gradually increasing. Up to T3, a total of 23 patients showed abnormal ECG.
| Parameters | T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 patients | 0 (0.00) | 15 (25.00) | 19 (31.67) | 23 (38.33) |
Table 1: ECG Abnormality Rate at 4 Time Points For 60 Breast Cancer Patients [n (%)]
Serum indexes at 4 time points for 60 breast cancer patients were shown here. As shown in Table 2 and fig. 2, the serum indexes perioperative period after chemotherapy and radiotherapy are lower than those before chemotherapy and radiotherapy, respectively.
| Parameters | T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White blood cell count (109/l) | 5.65±2.35 | 4.12±2.98 | 5.27±2.46 | 4.01±2.53 |
| Neutrophil absolute value (109/l) | 3.87±2.87 | 3.16±3.65 | 3.56±2.14 | 3.05±3.54 |
| Hemoglobin (g/l) | 111±3.65 | 98±2.78 | 105±3.42 | 95±2.58 |
| Platelet count (109/l) | 246±5.34 | 223±4.26 | 235±5.15 | 210±4.34 |
Table 2: Serum Indexes at 4 Time Points For 60 Breast Cancer Patients [n (%)]
Rate of adverse reactions in patients after treatment were shown in Table 3. It can be seen from Table 3 and fig. 3 that after chemotherapy and radiotherapy, there were 3 cases of radiation pneumonitis, 2 cases of pain and 2 cases of abnormal liver function during perioperative period. The total number of abnormal reaction cases was 9 and the total abnormal rate was 15 %.
| Item | Radiation pneumonitis | Pain | Abnormal liver function | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 patients | 3 (5.00) | 5 (8.33) | 1 (1.67) | 9 (15.00) |
Table 3: Rate of Adverse Reactions in Patients after Treatment [n (%)]
Breast cancer is a disease with high incidence of malignant tumor. The main clinical manifestations are irregular breast edge or hard unilateral breast development, areola and skin changes, which seriously threaten the life and health of patients. At present, the early diagnosis rate of breast cancer in China is relatively low, most patients are 50~60 y old and the incidence is increasing in younger. The traditional treatment is chemotherapy, but the curative effect will continue to decrease with the extension of patient’s treatment time[21]. There is a lack of surgical indications for advanced breast cancer. Therefore, radiotherapy and chemotherapy are often used to treat this disease. Breast cancer is a systemic disease with different molecular phenotypes, so there are differences in treatment and prognosis[22,23]. This study not only used chemotherapy intervention but also combined with trastuzumab for treatment.
In breast cancer patients with positive HER2, tumor cells proliferate, develop and spread rapidly, and are easily transferred to other tissues and organs[24,25]. Once metastasis occurs, conventional radiotherapy, chemotherapy and surgery cannot effectively control the local and systemic metastasis of cancer cells[26-28], because targeted drugs can specifically inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells, as they are often used in the treatment of breast cancer overexpression of HER2[13-15]. Trastuzumab is a targeted drug for HER2 proto-oncogene tumors. After intravenous administration, the antibody targets (specifically) tumor cells with overexpression of HER2 receptor and inhibits the interaction between growth factors and tumor cells[16-18]. This effect is due to the competitive inhibition mechanism of growth factor binding. The dissociation of HER2 receptor structure, the downregulation of HER2 receptor expression or the interference of HER2 receptor signaling pathway have the characteristics of rapid onset and selective killing of tumor cells, which can significantly improve the survival rate of breast cancer[13,16,18]. By acting on the extracellular portion of the HER2, the drug inhibits the formation of heterodimers of HER2 and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR), and blocks the activity of enzymes such as Protein kinase (Akt), thereby inactivating the proto-oncogene and ultimately preventing the development of cancer[15,17,18]. Compared with chemotherapy drugs, trastuzumab has the following mechanisms of action like, it block the activation of signal transduction pathways and inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer; inhibit the growth of vascular growth factors such as HER2, so as to promote the negative HER2. However, as a biological agent, trastuzumab has many adverse reactions[28-31], such as dyspnea, hypotension and tachycardia, among which cardiotoxicity is the most serious[32].
The results of this study showed that serum indexes during perioperative period after chemotherapy and radiotherapy are lower than those before chemotherapy and radiotherapy respectively. The abnormal ECG rate at T1, T2 and T3 was gradually increasing. Up to T3, a total of 23 patients showed abnormal ECG. It indicates that trastuzumab can improve serum level of breast cancer patients during perioperative period after chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy. However, the abnormal rate of ECG is associated with higher cardiotoxicity and more serious cardiac function damage, which may be related to HER2 signal peptide, whose downstream signal transduction pathway is closely related to normal cardiac function. Trastuzumab can inhibit the expression of HER2 protein and affect cardiac function, leading to heart failure. Therefore, patient’s cardiac function should be measured in real time during perioperative period[33,34].
In conclusion, postoperative chemotherapy and radiotherapy combined with trastuzumab can decrease serum levels in breast cancer patients during perioperative period. Meanwhile, the abnormal rate of ECG and cardiotoxicity were higher but there are few adverse reactions. Therefore, before trastuzumab is applied, cardiac function safety tests should be conducted in breast cancer patients and cardiac function of patients should be closely monitored.
Conflict of interests:
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
References
- Katsura C, Ogunmwonyi I, Kankam HK, Saha S. Breast cancer: Presentation, investigation and management. Br J Hosp Med 2022;83(2):1-7.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamann U, Ankel C. Mammakarzinom: Diagnostik und therapie-das wichtigste für den internisten [Breast Cancer: Diagnostics and therapy-the most important facts for internists]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 2018;143(4):267-78.
- Paizula X, Mutailipu D, Xu W, Wang H, Yi L. Identification of biomarkers related to tumorigenesis and prognosis in breast cancer. Gland Surg 2022;11(9):1472-88.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deng JL, Xu YH, Wang G. Identification of potential crucial genes and key pathways in breast cancer using bioinformatic analysis. Front Genet 2019;10:695.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morris M, Woods LM, Bhaskaran K, Rachet B. Do pre-diagnosis primary care consultation patterns explain deprivation-specific differences in net survival among women with breast cancer? an examination of individually-linked data from the UK West Midlands cancer registry, national screening programme and clinical practice research datalink. BMC Cancer 2017;17(1):155.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li Z, Zhang H, Wang X, Wang Q, Xue J, Shi Y, et al. Identification of cuproptosis-related subtypes, characterization of tumor microenvironment infiltration and development of a prognosis model in breast cancer. Front Immunol 2022;13:996836.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trayes KP, Cokenakes SEH. Breast cancer treatment. Am Fam Physician 2021;104(2):171-8.
[Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Waks AG, Winer EP. Breast cancer treatment: A review. JAMA 2019;321(3):288-300.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burstein HJ, Curigliano G, Thürlimann B, Weber WP, Poortmans P, Regan MM, et al. Customizing local and systemic therapies for women with early breast cancer: The St. Gallen international consensus guidelines for treatment of early breast cancer 2021. Ann Oncol 2021;32(10):1216-35.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reinert T, de Souza ABA, Sartori GP, Obst FM, Barrios CH. Highlights of the 17th St Gallen international breast cancer conference 2021: Customizing local and systemic therapies. Ecancermedicalscience 2021;15:1236.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomssen C, Balic M, Harbeck N, Gnant M. St. Gallen/Vienna 2021: A brief summary of the consensus discussion on customizing therapies for women with early breast cancer. Breast Care 2021;16(2):135-43.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li WD, Chen FF. Expression and significance of human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 and Ki-67 in breast cancer tissues. Matern Child Health Care China 2017;32(5):915-6.
- Padayachee J, Daniels A, Balgobind A, Ariatti M, Singh M. HER-2/neu and MYC gene silencing in breast cancer: Therapeutic potential and advancement in nonviral nanocarrier systems. Nanomedicine 2020;15(14):1437-52.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marchio C, Annaratone L, Marques A, Casorzo L, Berrino E, Sapino A. Evolving concepts in HER2 evaluation in breast cancer: Heterogeneity, HER2-low carcinomas and beyond. Semin Cancer Biol 2021;72:123-35.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee J, Park YH. Trastuzumab deruxtecan for HER2+ advanced breast cancer. Future Oncol 2022;18(1):7-19.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Modi S, Saura C, Yamashita T, Park YH, Kim SB, Tamura K, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2020;382(7):610-21.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Modi S. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: Plain language summary of the DESTINY-Breast01 study. Future Oncol 2021;17(26):3415-23.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang XM, Wang SZ, Ou JH. The efficacy and safety of trastuzumab combined with TC regimen in the treatment of HER-2 overexpressing breast cancer. Chin Med Herald 2018;15(11):104-7.
- Zhang LP, Wang B, Ma JW, Zhang HL. Efficacy and safety analysis of Liuwei dihuang decoction combined with docetaxel, capecitabine and trastuzumab in the treatment of advanced breast cancer patients. China Med 2019;14(1):96-9.
- Chinese anti-cancer association, Committee of breast cancer society. Guidelines and guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer of the Chinese anti-cancer association (2015 ed). China Oncol 2015;25(9):692-754.
- Xiao C, Zhang ZM, Sun SG. Clinical observation of trastuzumab combined with CAF chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced breast cancer. Clin J Med Offic 2019;47(4):368-70.
- Xu H, Dong J, Zhao J. Clinical effect of arterial infusion chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy for breast wall recurrence after modified radical breast cancer. J Prev Med Chin PLA 2019;37(10):54-5.
- Hou JF, Ren TJ, Liu C, Xue Q. Efficacy and safety of tegafur, gimeracil, oteracil potassium capsule combined with radiation sequential chemotherapy in treatment of abdominal lymph node metastases after gastrectomy. Eval Anal Drug Use Hosp China 2017;17(8):1056-60.
- Wang MJ. Trastuzumab and paclitaxel neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the treatment of HER-2-positive advanced local breast cancer. Henan Med Res 2018;27(7):1234-6.
- Tuo Y. Effect of trastuzumab combined with TP chemotherapy on postoperative breast cancer. Mod Med J 2018;46(5):537-40.
- Yin ZY, Zhang T, Qu GB. Efficacy evaluation of TP regimen combined with trastuzumab in treating human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer. Oncol Prog 2019;17(12):1391-94.
- Tan M, Xiang DH. Clinical efficacy and prognosis of trastuzumab combined with chemoradiotherapy in the treatment of advanced breast cancer with positive HER-2. Pract J Cancer 2018;33(10):1714-16.
- Liu H. Trastuzumab combined with docetaxel in the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Womens Health Res 2019;14(13):24-5.
- Zhou J, Hu X, Zhang H, Xiao J, Lin Q, Yuan Y, et al. Effect of trastuzumab combined with allium acyclic drugs on cardiac function in patients with HER-2 positive breast cancer. CJCPT 2019;26(10):707-12.
- He Y. Effect analysis of trastuzumab and chemotherapy in treatment of advanced breast cancer. J North Pharm 2018;15(11):54-5.
- Yuan L. Influence of trastuzumab combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy on clinical efficacy and related indexes after breast cancer surgery. J North Pharm 2018;15(1):44-5.
- Jiang Z, Wei W. Observation on the efficacy of trastuzumab and chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced breast cancer and evaluation on the incidence of adverse reactions. Contemp Med 2019;25(29):87-9.
- Guo Z, Zhou Q, Jiang A, Li X, Hu Q. Trastuzumab in neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer with positive HER-2 and its effect on tumor markers and immune function. Anti-Tumor Pharm 2017;9(1):98-102.
- Hui GY, Guo YR, Ruan WW. Effects of trastuzumab combined with docetaxel on serum tumor markers and immune function in patients with intermediate and advanced breast cancer with positive HER-2. Chin J Clin Oncol Rehabil 2019;26(11):1180-3.
 ECG abnormality rate at 4 time points for 60 breast cancer patients
ECG abnormality rate at 4 time points for 60 breast cancer patients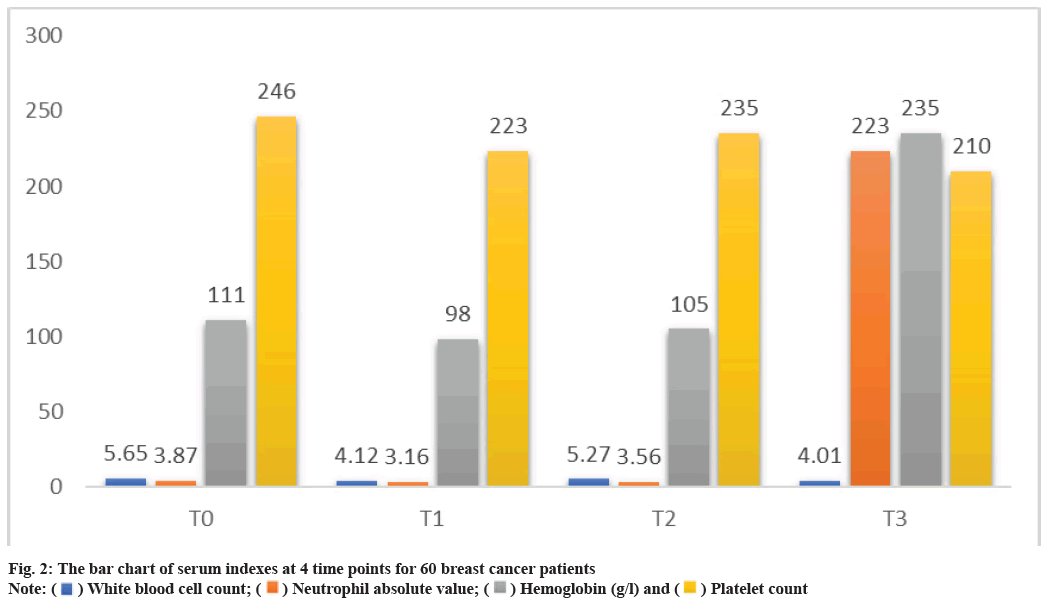
 White blood cell count;
White blood cell count;  Neutrophil absolute value;
Neutrophil absolute value;  Hemoglobin (g/l) and
Hemoglobin (g/l) and  Platelet count
Platelet count
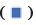 adverse reactions in patients after treatment
adverse reactions in patients after treatment



