- Corresponding Author:
- D. Purohit*
Padm. Dr. D. Y. Patil Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, Pimpri, Pune-411 018, India
E-mail: devang.purohit@ranbaxy.com
Abstract
The primary aim of present investigation was to develop and formulate room temperature stable formulation of formoterol fumarate and beclomethasone dipropionate with extra fine part size of hydrofluoroalkane pressurized metered dose inhalers. Particle size distribution of hydrofluoroalkane pressurized metered dose inhalers was evaluated using Twin Stage Glass Impinger and Anderson Cascade Impactor. A tetrafluoroethane and/or heptafluoropropane were evaluated for preparation of hydrofluoroalkane pressurized metered dose inhalers. The fine particle fractions delivered from hydrofluoroalkane propellant suspension pressurized metered dose inhalers can be predicted on the basis of formulation parameters and is dependent of metering chamber of valve and orifice size of actuators. The results presented in investigation showed the importance of formulation excipients with formulation of pressurized metered dose inhalers viz, canister, valve and actuators used in formulations.
Keywords
Impinger, aerosols, deposition of emitted dose, delivered dose uniformity
To develop room temperature stable formulation of formoterol fumarate/beclomethasone dipropionate hydrofluoroalkane (HFA) pressurized metered dose inhalers (pMDI) for lung delivery. The HFA pMDI were prepared from ozone friendly propellants viz, tetrafluoroethane and/or heptafluoropropane. A HFA based formulation of formoterol fumarate/ beclomethasone dipropionate was developed to deliver 6 +100/200 µg per actuation over 120 doses. The present formulation comprises polyvinylpyrrolidone and/or polyethylene glycol in an amount sufficient to enhance the physical stability of suspension and provide extra fi ne particle size of formoterol fumarate/ beclomethasone dipropionate. Formoterol fumarate and beclomethasone dipropionate have different modes of action. Beclomethasone dipropionate, a synthetic glucocorticoid given by inhalation at recommended doses has an antiinflammatory action, which plays an important role in the effi cacy of beclomethasone dipropionate in controlling symptoms and improving lung function in asthma. Inhaled beclomethasone dipropionate probably acts topically at the site of deposition in the bronchial tree after inhalation. Formoterol is a selective ß2 adrenergic agonist that produces relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle in patients with reversible airways obstruction. In addition to its bronchodilator action, formoterol also inhibits mast cell mediator release, plasma exudation and may reduce sensory nerve activation. Thus these two classes of drug address complementary aspects of the pathophysiology of asthma and COPD that neither drug class is able to achieve alone.
Materials and Methods
Excipients selected for evaluation were polyethylene glycol (at levels of 0.05 to 2.5% w/w, supplied by Clariant, India) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (at levels of 0.002 to 0.5% w/ w, supplied by Signet, India). The amount of micronised formoterol fumarate and beclomethasone dipropionate were mixed in a pressure vessel in a way to get the appropriate dose of formoterol fumarate and beclomethasone dipropionate to be able to deliver the desired doses to the patient. Beclometasone dipropionate/formoterol fumarate in above formulation is characterized by an extra-fi ne particle size distribution which results in a more potent effect than individual formulation of beclomethasone available in market. The above combination is indicated for regular treatment of asthma where use of a combination product (inhaled corticosteroid and long-acting beta2-agonist) is appropriate.
pMDIs were prepared by single step manufacturing process as given here: Introduction of active/ excipients into pressure vessel, Addition of required quantity of propellant to provide sufficient number of doses, Filling of drug/propellant mixture into precrimped aluminum canister (supplied by Presspart, UK).
Results and Discussion
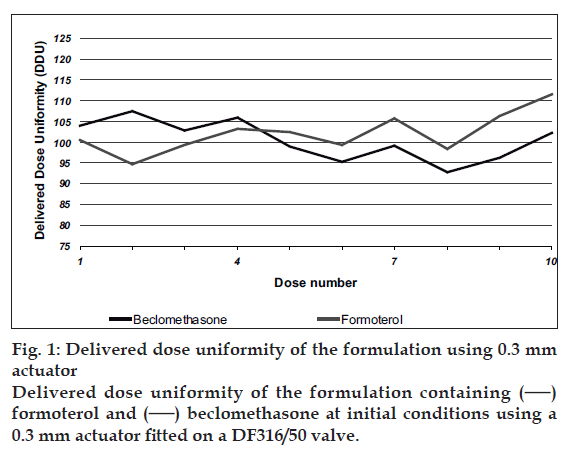
Delivered dose uniformity results obtained with a DF316/50 valve fitted with a 0.3 mm outlet orifice diameter actuator are shown in fig. 1 and those obtained with a DF316/50 valve fitted with a 0.48 mm outlet orifice diameter actuator are shown in fig. 2. Deposition of emitted dose by TSLI results are summarized in Table 1. During this study, Polyethylene glycol at levels less than 0.5% w/w was found to ensure good product performances and valve functioning throughout the MDI units? life. The level of polyvinylpyrrilodone selected also helped to decrease the settling of particles and prevents agglomeration of actives. This formulation was readily re-dispersible and avoiding invariability dosing of the drug. The stable suspension of particulate beclomethasone/ formoterol fumarate was selected by us ing HFA propellants closely matching the density of the micronised actives.
| Drug | 0.3 mm Actuator | 0.48 mm Actuator |
|---|---|---|
| Beclomethasone | 40.23% | 49.89% |
| dipropionate | ||
| Formoterol fumarate | 56.81% | 69.03% |
Values are in terms of % of Label Claim
Table 1: Deposition of Emitted Dose by Tsli
In conclusion, the novel combination of formoterol fumarate and beclomethasone dipropionate is a suspension based HFA pMDI product. The combined characteristics of room temperature stable formulation with good deposition of both drugs in lung provides unique characteristics to the above fixed dose combination, highly attractive in terms of patient usage requirements and commercial supply.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Valois, France & Presspart, UK for supplying canisters and valves for development trials.
References
- Purewal T. Formulation of metered dose inhalers, Metered dose inhalers technology, Buffalo Grove: Interpharm Press; 1998, p. 1-8.
- Vervaet C, Byron PR. Drug-surfactant-propellant interactions in HFAformulations. Int J Pharm 1999;186:13-30.
- Hickey AJ. Inhalation Aerosols, Physical and Biological Basis for Therapy, 2nd ed. In; Lenfant C. Editors. Lung Biology in Health and Disease. Vol. 221. Boca Raton: In-forma Health Care; 2007.
- Murnane D, Martin GP, Marriott C. Investigations into the Formulation of Metered Dose Inhalers of Salmeterol Xinafoate and Fluticasone Propionate Microcrystals. Pharm Res 2008;25:2283-91.